Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The work function for a metal surface is 2.2eV. If the light of wavelength 5000Å is incident on the surface of the metal, find the threshold frequency and incident frequency. Will there be an emission of photoelectrons or not? (c = 3 x 108 m/ s, 1eV = 1.6x10-19 J , h = 6.63 x 10-34 J.s.)
उत्तर
Given work function = `Φ_0` = 2.2 eV
= `2.2 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19) J`
= `3.52 xx 10^(-19)`
λ = 500 Å = 5000 x 10-10 m, c = `3xx10^8` m/s, h = `6.63 xx 10^(-34) Js`
Incident frequency v = `c/λ = (3xx10^8)/(5000 xx 10^(-10)`
= `(3xx10^8)/(5xx10^(-7) )= 3/5 xx 10^(-15) Hz`
=`30/5 xx 10^(14) Hz = 6 xx 10^(14) Hz`
Threshold frequency v0 = `Φ_0/h = (3.52 xx 10^(-19) J)/(6.63 xx 10^(-34) Js`
= `0.53 xx 10^15 Hz = 5.3 xx 10^14 Hz`
Emission of photoelectron takes place only if incident frequency is greater than the threshold frequency. But, in this case n>n0 therfore, photoelectric emission takes place.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The energy of photon of wavelength X is_____ .
[h = Planck’s constant, c = speed of light in vacuum]
The threshold wavelength of silver is 3800Å. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy in eV of photoelectrons emitted, when ultraviolet light of wavelength 2600Å falls on it.
(Planck’s constant, h =6.63 x 1O-34J.s.,
Velocity of light in air, c = 3 x 108 m / s)
The momentum of a photon of de Broglie wavelength 5000Å is _______.
[Planck’s constant = 6.63 x10-34 J.s.]
When radiations of wavelength λ1 and λ2 are incident on certain photosensitive, such that E1 > E2 . Then Planck's constant 'h' is ......................... .
(C = Velocity of light).
Find the wave number of a photon having energy of 2.072 eV
Given : Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C,
Velocity of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s.
Define (i) stopping potential and (ii) threshold frequency, using Einstein’s equation and drawing necessary plot between relevant quantities.
Write Einstein's photoelectric equation and mention which important features in photoelectric effect can be explained with the help of this equation.
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons gets doubled when the wavelength of light incident on the surface changes from λ1 to λ2. Derive the expressions for the threshold wavelength λ0 and work function for the metal surface.
A proton and a deuteron are accelerated through the same accelerating potential. Which one of the two has less momentum?
Give reasons to justify your answer.
Radiation of frequency 1015 Hz is incident on two photosensitive surface P and Q. There is no photoemission from surface P. Photoemission occurs from surface Q but photoelectrons have zero kinetic energy. Explain these observations and find the value of work function for surface Q.
With reference to the photoelectric effect, define threshold wavelength
Write the basic features of photon picture of electromagnetic radiation on which Einstein’s photoelectric equation is based.
Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
According to Einstein’s model, the threshold frequency for a metal having work function ϕ0 is given by _________.
Which of the following graphs correctly represents the variation of maximum kinetic energy (Ek) of photoelectrons with the frequency (𝜈) of the incident radiation?
Plot a labelled graph of |Vs| where Vs is stopping potential versus frequency f of the incident radiation. State how will you use this graph to determine the value of Planck's constant?
A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km/h fires a bullet at a thief's car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of 192 km/h. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is 150 m is, with what speed does the bullet hit the thief's car?
In an inelastic collision, which of the following does not remain conserved?
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal Vs the frequency of the incident radiation gives as straight the whose slope:
A 200 W sodium street lamp emits yellow light of wavelength 0.6 µm. Assuming it to be 25% efficient in converting electrical energy to light, the number of photons of yellow light it emits per second is:
Threshold frequency for photoelectric effect on sodium corresponds to a wave length 5000. Its work function is ______.
If the energy of photon corresponding to a wavelength of 6000 A° is 3.32 × 10-19 J, the photon energy for a wavelength of 4000 A° will be
Which of the following is/are true for cathode ray
(i) A ray of light incident on face AB of an equilateral glass prism, shows minimum deviation of 30°. Calculate the speed of light through the prism.
(ii) Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
How does stopping potential in photoelectric emission vary if the intensity of the incident radiation increases?
The graphs below show the variation of the stopping potential VS with the frequency (ν) of the incident radiations for two different photosensitive materials M1 and M2.
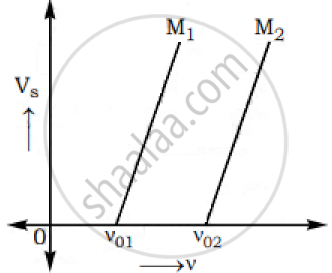
Express work function for M1 and M2 in terms of Planck’s constant(h) and Threshold frequency and charge of the electron (e).
If the values of stopping potential for M1 and M2 are V1 and V2 respectively then show that the slope of the lines equals to `(V_1-V_2)/(V_(01)-V_(02))` for a frequency,
ν > ν02 and also ν > ν01
