Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two particles are projected in air with speed vo at angles θ1 and θ2 (both acute) to the horizontal, respectively. If the height reached by the first particle is greater than that of the second, then tick the right choices
- Angle of projection: q1 > q2
- Time of flight: T1 > T2
- Horizontal range: R1 > R2
- Total energy: U1 > U2
उत्तर
a and b
Explanation:
According to formula, Max height of a projectile is
H = `(u^2 sin^2 theta)/(2g)`
a. `H_1 > H_2`
`sin^2 theta_1 > sin^2 theta_2`
`(sin theta_1 + sin theta_2) (sin theta_1 - sin theta_2) > 0`
So, `(sin theta_1 + sin theta_2) > 0` or `(sin theta_1 - sin theta_2) > 0`
So, `θ_1 > θ_2` and θ lies between 0 and 90 degree i.e. acute
b. `T_1/T_2 = sin theta_1/sin theta_2`
`T_1/T_2 = sin theta_1/sin theta_2`
`T_1 sin theta_2 = T_2 sin theta_1`
Since sin θ1 > sin θ2
T1 > T2
Important points about the time of flight: For complementary angles of projection θ and 90° – θ.
a. Ratio of time flight = `T_1/T_2`
= `(2 u sin theta/g)/(2u sin (90^circ - theta)/g)`
= tan θ
⇒ `T_1/T_2` = tan θ
b. Multiplication of time of flight = `T_1T_2`
= `(2u sin theta)/g (2u cos theta)/g`
⇒ `T_1T_2 = (2R)/g`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An aircraft is flying at a height of 3400 m above the ground. If the angle subtended at a ground observation point by the aircraft positions 10.0 s a part is 30°, what is the speed of the aircraft?
The horizontal range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be ______.
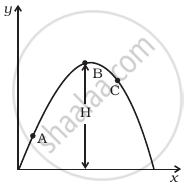
A particle is projected in air at some angle to the horizontal, moves along parabola as shown in figure, where x and y indicate horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. Show in the diagram, direction of velocity and acceleration at points A, B and C.
A boy travelling in an open car moving on a levelled road with constant speed tosses a ball vertically up in the air and catches it back. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by a boy standing on the footpath. Give explanation to support your diagram.
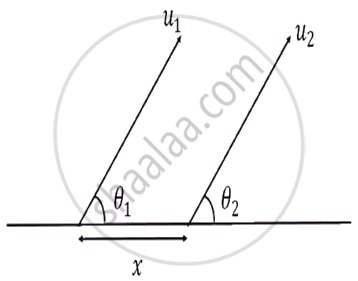
Two particles are projected simultaneously from the level ground as shown in figure. They may collide after a time:
If a baseball player can throw a ball at maximum distance = d over a ground, the maximum vertical height to which he can throw it, will be (Ball has same initial speed in each case):
Two stones are projected with the same speed but making different angles with the horizontal. Their ranges are equal. If the angle of projection of one is `pi/3` and its maximum height is y1 then the maximum height of the other will be ______.
A person standing on a truck moving with a uniform velocity of 14.7 ms-1 on a horizontal road throws a ball in such a way that it returns to him after 4s. Find the speed and angle of projection as seen by a man on the road ______.
An object is projected in the air with initial velocity u at an angle θ. The projectile motion is such that the horizontal range R, is maximum.
Another object is projected in the air with a horizontal range half of the range of first object. The initial velocity remains same in both the case. The value of the angle of projection, at which the second object is projected, will be ______ degree.
The initial speed of a bullet fired from a rifle is 630 m/s. The rifle is fired at the centre of a target 700 m away at the same level as the target. How far above the centre of the target the rifle must be aimed in order to hit the target?
