Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A boy travelling in an open car moving on a levelled road with constant speed tosses a ball vertically up in the air and catches it back. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by a boy standing on the footpath. Give explanation to support your diagram.
उत्तर
Let the vertical velocity of the tossed ball be v and the speed of the car be u which must be equal to the horizontal velocity of the ball.
The ball has both components of motion, hence it will have a parabolic trajectory when observed from a distance. This can be shown in the figure below.
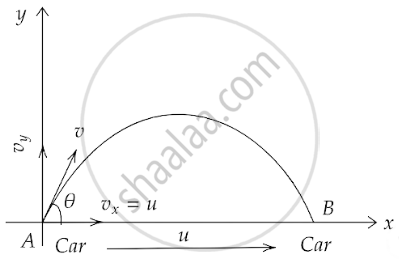
When this motion is observed by the boy sitting in the car, it will look like only a vertically up-down motion and he will catch the ball when it comes back to the ground if the car has a constant velocity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An aircraft is flying at a height of 3400 m above the ground. If the angle subtended at a ground observation point by the aircraft positions 10.0 s a part is 30°, what is the speed of the aircraft?
A cricket ball thrown across a field is at heights h1 and h2 from the point of projection at times t1 and t2 respectively after the throw. The ball is caught by a fielder at the same height as that of projection. The time of flight of the ball in this journey is
A particle moving in a circle of radius R with a uniform speed takes a time T to complete one revolution.
If this particle were projected with the same speed at an angle ‘θ’ to the horizontal, the maximum height attained by it equals 4R. The angle of projection, θ, is then given by ______.
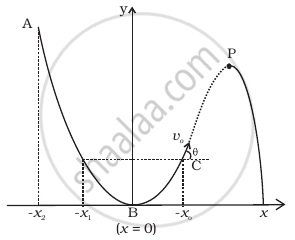
A particle slides down a frictionless parabolic (y = x2) track (A – B – C) starting from rest at point A (Figure). Point B is at the vertex of parabola and point C is at a height less than that of point A. After C, the particle moves freely in air as a projectile. If the particle reaches highest point at P, then
A ball is thrown from a roof top at an angle of 45° above the horizontal. It hits the ground a few seconds later. At what point during its motion, does the ball have
- greatest speed.
- smallest speed.
- greatest acceleration?
Explain
A cricket fielder can throw the cricket ball with a speed vo. If he throws the ball while running with speed u at an angle θ to the horizontal, find
- the effective angle to the horizontal at which the ball is projected in air as seen by a spectator.
- what will be time of flight?
- what is the distance (horizontal range) from the point of projection at which the ball will land?
- find θ at which he should throw the ball that would maximise the horizontal range as found in (iii).
- how does θ for maximum range change if u > vo, u = vo, u < vo?
- how does θ in (v) compare with that for u = 0 (i.e.45)?
The minimum speed in m/s with which a projectile must be thrown from origin at ground so that it is able to pass through a point P (30 m, 40 m) is ______. (g = 10 m/s2)
A person standing on a truck moving with a uniform velocity of 14.7 ms-1 on a horizontal road throws a ball in such a way that it returns to him after 4s. Find the speed and angle of projection as seen by a man on the road ______.
An object is projected in the air with initial velocity u at an angle θ. The projectile motion is such that the horizontal range R, is maximum.
Another object is projected in the air with a horizontal range half of the range of first object. The initial velocity remains same in both the case. The value of the angle of projection, at which the second object is projected, will be ______ degree.
The initial speed of a bullet fired from a rifle is 630 m/s. The rifle is fired at the centre of a target 700 m away at the same level as the target. How far above the centre of the target the rifle must be aimed in order to hit the target?
