Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball is thrown from a roof top at an angle of 45° above the horizontal. It hits the ground a few seconds later. At what point during its motion, does the ball have
- greatest speed.
- smallest speed.
- greatest acceleration?
Explain
उत्तर
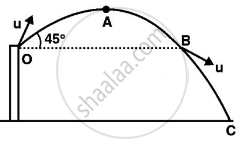
In this problem total mechanical energy of the ball is conserved. As the ball is projected from point O and covers the path OABC.
At point A it has both kinetic and potential energy.
But at point C it has only kinetic energy, (keeping the ground as a reference where PE is zero.)
- At point B, it will gain the same speed as u and after that speed increases and will be maximum just before reaching C.
- During the upward journey from O to A speed decreases and the smallest speed attained by it is at the highest point, i.e., at point A.
- Acceleration is always constant throughout the journey and is vertically downward equal to g.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100 m. How much high above the ground can the cricketer throw the same ball?
Show that the projection angle `theta_o` for a projectile launched from the origin is given by
`theta_o =tan^(-1) ((4h_m)/R)`
Where the symbols have their usual meaning
A particle moving in a circle of radius R with a uniform speed takes a time T to complete one revolution.
If this particle were projected with the same speed at an angle ‘θ’ to the horizontal, the maximum height attained by it equals 4R. The angle of projection, θ, is then given by ______.
The horizontal range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be ______.
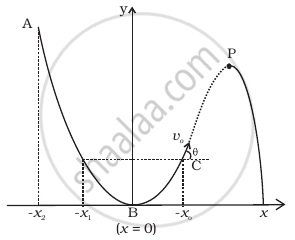
A particle slides down a frictionless parabolic (y = x2) track (A – B – C) starting from rest at point A (Figure). Point B is at the vertex of parabola and point C is at a height less than that of point A. After C, the particle moves freely in air as a projectile. If the particle reaches highest point at P, then
A particle is projected in air at some angle to the horizontal, moves along parabola as shown in figure, where x and y indicate horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. Show in the diagram, direction of velocity and acceleration at points A, B and C.
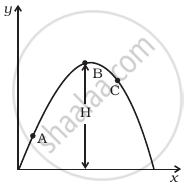
A football is kicked into the air vertically upwards. What is its acceleration?
Two stones are projected with the same speed but making different angles with the horizontal. Their ranges are equal. If the angle of projection of one is `pi/3` and its maximum height is y1 then the maximum height of the other will be ______.
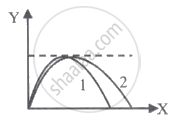
The trajectories of the two projectiles are shown in the figure. Let T1 and T2 be the time periods and u1 and u2 be their speeds of projection. Then ______.