Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ball is thrown from a roof top at an angle of 45° above the horizontal. It hits the ground a few seconds later. At what point during its motion, does the ball have
- greatest speed.
- smallest speed.
- greatest acceleration?
Explain
Solution
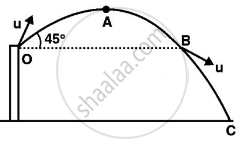
In this problem total mechanical energy of the ball is conserved. As the ball is projected from point O and covers the path OABC.
At point A it has both kinetic and potential energy.
But at point C it has only kinetic energy, (keeping the ground as a reference where PE is zero.)
- At point B, it will gain the same speed as u and after that speed increases and will be maximum just before reaching C.
- During the upward journey from O to A speed decreases and the smallest speed attained by it is at the highest point, i.e., at point A.
- Acceleration is always constant throughout the journey and is vertically downward equal to g.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A cricket ball thrown across a field is at heights h1 and h2 from the point of projection at times t1 and t2 respectively after the throw. The ball is caught by a fielder at the same height as that of projection. The time of flight of the ball in this journey is
The horizontal range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be ______.
Two particles are projected in air with speed vo at angles θ1 and θ2 (both acute) to the horizontal, respectively. If the height reached by the first particle is greater than that of the second, then tick the right choices
- Angle of projection: q1 > q2
- Time of flight: T1 > T2
- Horizontal range: R1 > R2
- Total energy: U1 > U2
A boy throws a ball in air at 60° to the horizontal along a road with a speed of 10 m/s (36 km/h). Another boy sitting in a passing by car observes the ball. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by the boy in the car, if car has a speed of (18 km/h). Give explanation to support your diagram.
A fighter plane is flying horizontally at an altitude of 1.5 km with speed 720 km/h. At what angle of sight (w.r.t. horizontal) when the target is seen, should the pilot drop the bomb in order to attack the target?
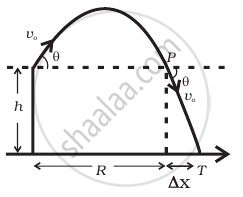
A gun can fire shells with maximum speed v0 and the maximum horizontal range that can be achieved is R = `v_0^2/g`. If a target farther away by distance ∆x (beyond R) has to be hit with the same gun (Figure), show that it could be achieved by raising the gun to a height at least `h = Δx[ 1 + (Δx)/R]`
A football is kicked into the air vertically upwards. What is its velocity at the highest point?
If a baseball player can throw a ball at maximum distance = d over a ground, the maximum vertical height to which he can throw it, will be (Ball has same initial speed in each case):
A body is thrown from a point with speed 50 m/s at an angle 37° with horizontal. When it has moved a horizontal distance of 80 m then its distance from point of projection is ______.
An object is projected in the air with initial velocity u at an angle θ. The projectile motion is such that the horizontal range R, is maximum.
Another object is projected in the air with a horizontal range half of the range of first object. The initial velocity remains same in both the case. The value of the angle of projection, at which the second object is projected, will be ______ degree.
