Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A boy throws a ball in air at 60° to the horizontal along a road with a speed of 10 m/s (36 km/h). Another boy sitting in a passing by car observes the ball. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by the boy in the car, if car has a speed of (18 km/h). Give explanation to support your diagram.
Solution
The situation is shown in the below diagram.
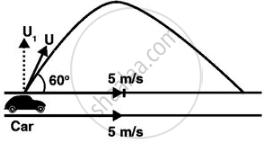
According to the problem, the boy standing on the ground throws the ball at an angle of 60° horizontal at a speed of 10 m/s.
∴ The horizontal component of velocity, ux = 10 cos θ
ux = (10 m/s) cos 60° = `10 xx 1/2` = 5 m/s
The vertical component of velocity, uy = 10 sin θ
uy = (10 m/s) sin 60° = `10 xx sqrt(3)/2 = 5sqrt(3)` m/s
Speed of the car = 18 km/h = 5 m/s
As the horizontal speed of ball and car is same, hence the relative velocity of ball w.r.t car in the horizontal direction will be zero.
Only the vertical motion of the ball will be observed by the boy in the car, as shown in the above diagram.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
The ceiling of a long hall is 25 m high. What is the maximum horizontal distance that a ball thrown with a speed of 40 m s–1 can go without hitting the ceiling of the hall?
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100 m. How much high above the ground can the cricketer throw the same ball?
An aircraft is flying at a height of 3400 m above the ground. If the angle subtended at a ground observation point by the aircraft positions 10.0 s a part is 30°, what is the speed of the aircraft?
A ball rolls of the top of the stairway with a horizontal velocity u ms−1. If the steps are h m high and b m wide, the ball will hit the edge of the nth step, if:
The minimum speed in m/s with which a projectile must be thrown from origin at ground so that it is able to pass through a point P (30 m, 40 m) is ______. (g = 10 m/s2)
A body starts from rest with constant acceleration a, its velocity after n second is v. The displacement of body in last two seconds is ______.
A circular disc of radius r = 5m is rotating in horizontal plane about y-axis. Y-axis is vertical axis passing through the centre of disc and x-z is the horizontal plane at ground. The height of disc above ground is h = 5 m. Small particles are ejecting from disc in horizontal direction with speed 12 m/s from the circumference of disc then the distance of these particles from origin when they hits the x-z plane is:
Two stones are projected with the same speed but making different angles with the horizontal. Their ranges are equal. If the angle of projection of one is `pi/3` and its maximum height is y1 then the maximum height of the other will be ______.
An object is projected in the air with initial velocity u at an angle θ. The projectile motion is such that the horizontal range R, is maximum.
Another object is projected in the air with a horizontal range half of the range of first object. The initial velocity remains same in both the case. The value of the angle of projection, at which the second object is projected, will be ______ degree.
