Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
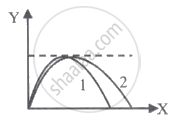
A boy travelling in an open car moving on a levelled road with constant speed tosses a ball vertically up in the air and catches it back. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by a boy standing on the footpath. Give explanation to support your diagram.
Solution
Let the vertical velocity of the tossed ball be v and the speed of the car be u which must be equal to the horizontal velocity of the ball.
The ball has both components of motion, hence it will have a parabolic trajectory when observed from a distance. This can be shown in the figure below.
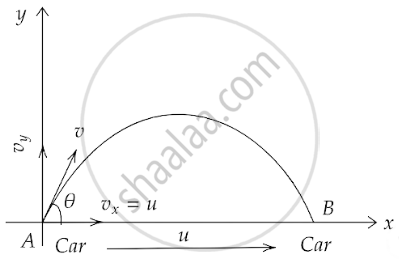
When this motion is observed by the boy sitting in the car, it will look like only a vertically up-down motion and he will catch the ball when it comes back to the ground if the car has a constant velocity.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
Show that the projection angle `theta_o` for a projectile launched from the origin is given by
`theta_o =tan^(-1) ((4h_m)/R)`
Where the symbols have their usual meaning
A body of mass m is projected horizontally with a velocity v from the top of a tower of height h and it reaches the ground at a distance x from the foot of the tower. If the second body of mass of 4 m is projected horizontally from the top of a tower of the height of 4 h, it reaches the ground at a distance of 4x from the foot of the tower. The horizontal velocity of the second body is:
A car starts from rest and accelerates at 5 m/s2. At t = 4 s, a ball is dropped out of a window by a person sitting in the car. What is the velocity and acceleration of the ball at t = 6 s? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
A car starts from rest and accelerates at 5 m/s2. At t = 4 s, a ball is dropped out of a window by a person sitting in the car. What is the velocity and acceleration of the ball at t = 6 s? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
A particle is projected in air at an angle β to a surface which itself is inclined at an angle α to the horizontal (Figure).
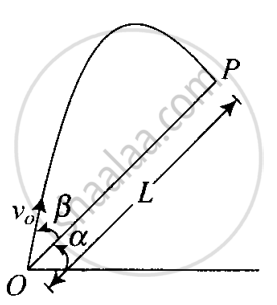
- Find an expression of range on the plane surface (distance on the plane from the point of projection at which particle will hit the surface).
- Time of flight.
- β at which range will be maximum.
A girl riding a bicycle with a speed of 5 m/s towards north direction, observes rain falling vertically down. If she increases her speed to 10 m/s, rain appears to meet her at 45° to the vertical. What is the speed of the rain? In what direction does rain fall as observed by a ground based observer?
A cricket fielder can throw the cricket ball with a speed vo. If he throws the ball while running with speed u at an angle θ to the horizontal, find
- the effective angle to the horizontal at which the ball is projected in air as seen by a spectator.
- what will be time of flight?
- what is the distance (horizontal range) from the point of projection at which the ball will land?
- find θ at which he should throw the ball that would maximise the horizontal range as found in (iii).
- how does θ for maximum range change if u > vo, u = vo, u < vo?
- how does θ in (v) compare with that for u = 0 (i.e.45)?
A person standing on a truck moving with a uniform velocity of 14.7 ms-1 on a horizontal road throws a ball in such a way that it returns to him after 4s. Find the speed and angle of projection as seen by a man on the road ______.
The trajectories of the two projectiles are shown in the figure. Let T1 and T2 be the time periods and u1 and u2 be their speeds of projection. Then ______.