Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two sine waves travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of each wave is A and the phase difference between the two waves is 120°. The resultant amplitude will be
विकल्प
A
2A
4A
उत्तर
A
We know the resultant amplitude is given by
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the formula
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the transmitted sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
(i) For the wave on a string described in Exercise 15.11, do all the points on the string oscillate with the same (a) frequency, (b) phase, (c) amplitude? Explain your answers. (ii) What is the amplitude of a point 0.375 m away from one end?
A wire stretched between two rigid supports vibrates in its fundamental mode with a frequency of 45 Hz. The mass of the wire is 3.5 × 10–2 kg and its linear mass density is 4.0 × 10–2 kg m–1. What is (a) the speed of a transverse wave on the string, and (b) the tension in the string?
Show that for a wave travelling on a string
where the symbols have usual meanings. Can we use componendo and dividendo taught in algebra to write
A sine wave is travelling in a medium. A particular particle has zero displacement at a certain instant. The particle closest to it having zero displacement is at a distance
Choose the correct option:
Which of the following equations represents a wave travelling along Y-axis?
Two wires A and B, having identical geometrical construction, are stretched from their natural length by small but equal amount. The Young modules of the wires are YA and YB whereas the densities are
Two wave pulses travel in opposite directions on a string and approach each other. The shape of one pulse is inverted with respect to the other.
The equation of a wave travelling on a string stretched along the X-axis is given by
(a) Write the dimensions of A, a and T. (b) Find the wave speed. (c) In which direction is the wave travelling? (d) Where is the maximum of the pulse located at t = T? At t = 2 T?
A wave pulse is travelling on a string with a speed
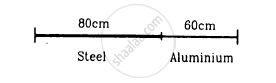
Figure shows an aluminium wire of length 60 cm joined to a steel wire of length 80 cm and stretched between two fixed supports. The tension produced is 40 N. The cross-sectional area of the steel wire is 1⋅0 mm2 and that of the aluminium wire is 3⋅0 mm2. What could be the minimum frequency of a tuning fork which can produce standing waves in the system with the joint as a node? The density of aluminium is 2⋅6 g cm−3 and that of steel is 7⋅8 g cm−3.
The equation for the vibration of a string, fixed at both ends vibrating in its third harmonic, is given by
(a) What is the frequency of vibration? (b) What are the positions of the nodes? (c) What is the length of the string? (d) What is the wavelength and the speed of two travelling waves that can interfere to give this vibration?
An organ pipe of length 0.4 m is open at both ends. The speed of sound in the air is 340 m/s. The fundamental frequency is ______
What is the interference of sound waves?
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of 4 m.
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of 0.5 m.
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
