Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Use ruler and compasses only for the following questions. All constructions lines and arcs must be clearly shown
Construct the locus of points equidistant from AC and BC.
उत्तर
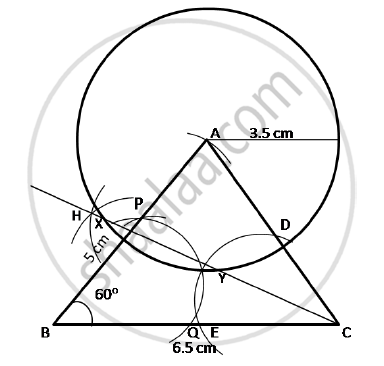
Steps for construction :
1) With C as the centre and with the radius of a length less than CA or BC, draw an arc to cut the line segments AC and BC at D and E respectively.
2) With the same radius or a suitable radius and with D as the centre, draw an arc of a circle.
3) With the same radius and with E as the centre draw an arc such that the two arcs intersect at H.
4) Join C and H.
5) CH is the bisector of ÐACB and is the required locus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use ruler and compasses only for the following questions. All constructions lines and arcs must be clearly shown.
Construct the locus of points at a distance of 3.5 cm from A.
A point moves such that its distance from a fixed line AB is always the same. What is the relation between AB and the path travelled by the point?
State the locus of a point moving so that its perpendicular distances from two given lines is always equal.
AB is a fixed line) state the locus of the point P such that ∠ APB = 90° .
The bisector of ∠ B and ∠C of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect in P, show that P is equidistant from the opposite sides AB and CD.
In ΔABC, the bisector AX of ∠A intersects BC ar X. XL ⊥ AB and XM ⊥ AC are drawn (Fig.) is XL = XM? why or why not?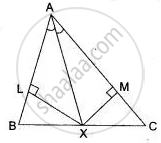
l is the perpendicular bisector of line segment PQ and R is a point on the same side of l as P. The segment QR intersects l at X. Prove that PX + XR = QR.
Given a Δ ABC with unequal sides. Find a point which is equidistant from B and C as well as from AB and AC.
The diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles. Show that the quadrilateral is a rhombus.
What is the locus of points which are equidistant from the given non-collinear point A, B and C? Justify your answer.
