Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
उत्तर
\[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]^{3+}}\]:
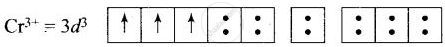
(i) Hybridisation – d2sp3
(ii) Inner orbital complex
(iii) Paramagnetic
(iv) Magnetic moment = `sqrt(3(3 + 2))` = 3.87 B.M
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Fe(CN)6]4−
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[CoF6]3−
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Mn(CN)6]^{3-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Write the hybridization and shape of the following complexes:
[Ni(CN)4]2−
When the hybridization state of carbon changes from sp3 to sp2 and finally to sp, the angle between hybridized orbital will
Which of the following has square planar structures?
Valence bond theory is based on the assumption that the bonds formed between the metal ions and ligands are ______
Using Valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the paramagnetic complex [Mn(CN)6]3-
- type of hybridization
- magnetic moment value
- type of complex – inner, outer orbital complex
Using valence bond theory, predict the hybridization and magnetic character of the following:
[CoF6]3– [Atomic number of Co = 27]
The magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2− is ______.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
