Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Water flows through a tube shown in figure. The area of cross section at A and B are 1 cm2 and 0.5 cm2 respectively. The height difference between A and B is 5 cm. If the speed of water at A is 10 cm s find (a) the speed at B and (b) the difference in pressures at A and B.

उत्तर
Given:
Difference in the heights of A and B = 5 cm
Area of cross section at A, aa = 1 cm2
Area of cross section at B, ab = 0.5 cm2
Speed of water at A, \[v_A\]=10 cms
(a) From the equation of continuity, we have:
\[ \vec{V}_A \times a_A = \vec{V}_B \times a_B \]
\[ \Rightarrow 10 \times 1 = \vec{V}_B \times 0 . 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec{V}_B = 20 \text{ cm}/s\]
The required speed of water at cross section B is 20 cms
(b) From Bernoulli's equation, we get:
\[ \frac{1}{2}\rho v_A^2 + ρ g h_A + P_A = \frac{1}{2}\rho v_B^2 + ρ g h_A + P_B \]
\[ \Rightarrow P_B - P_A = \frac{1}{2}\rho\left( v_A^2 - v_B^2 \right) + ρg\left( h_A - h_B \right)\]
Here,
PA and PB are the pressures at A and B, respectively.
hA and hB are the heights of points A and B, respectively.
ρ is the density of the liquid.
On substituting the values, we have:
\[P_B - P_A = \frac{1}{2} \times 1(100 - 400) + 1 \times 1000(5 . 0)\]
\[ = - 150 + 5000 = 4850 \text{ Dyne}/ {cm}^2 \]
\[ = 485 N/ m^2\]
herefore, the required pressure difference at A and B is 485 N/m2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
While watering a distant plant, a gardener partially closes the exit hole of the pipe by putting his finger on it. Explain why this results in the water stream going to a larger distance.
At Deoprayag (Garwal, UP) river Alaknande mixes with the river Bhagirathi and becomes river Ganga. Suppose Alaknanda has a width of 12 m, Bhagirathi has a width of 8 m and Ganga has a width of 16 m. Assume that the depth of water is same in the three rivers, Let the average speed of water in Alaknanda be 20 km/h and in Bhagirathi be 16 km/h. Find the average speed of water in the river Ganga.
Water flows through a horizontal tube as shown in figure. If the difference of heights of water column in the vertical tubes is 2 cm, and the areas of cross section at A and B are 4 cm2 and 2 cm2 respectively, find the rate of flow of water across any section.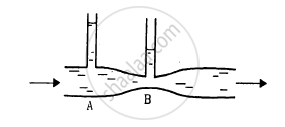
Water flows through the tube shown in figure. The areas of cross section of the wide and the narrow portions of the tube are 5 cm2 and 2 cm2 respectively. The rate of flow of water through the tube is 500 cm3 s−1. Find the difference of mercury levels in the U-tube.
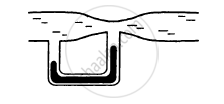
A vessel completely filled with water has holes 'A' and 'B' at depths 'h' and '3h' from the top respectively. Hole 'A' is a square of side 'L' and 'B' is a circle of radius 'r'. The water flows out per second from both the holes in the same. Then 'L' is equal to ______.
An ideal fluid flows through a pipe of circular cross-section made of two sections with diameters 2.5 cm and 3.75 cm. The ratio of the velocities in the two pipes is ______.
Explain the continuity condition for a flow tube. Show that the flow speed is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of a flow tube.
