Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
उत्तर १
There are two common types of secondary structure of proteins:
(i) ∝-helix structure
(ii) β-pleated sheet structure
∝- Helix structure:
In this structure, the −NH group of an amino acid residue forms H-bond with the 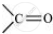 group of the adjacent turn of the right-handed screw (∝-helix).
group of the adjacent turn of the right-handed screw (∝-helix).

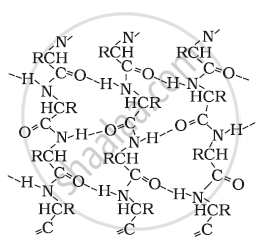
β-pleated sheet structure:
This structure is called so because it looks like the pleated folds of drapery. In this structure, all the peptide chains are stretched out to nearly the maximum extension and then laid side by side. These peptide chains are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
उत्तर २
The conformation which the polypeptide chains assume as a result of hydrogen bonding is called secondary structure of the proteins. The two types of secondary structures are α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is peptide linkage?
Differentiate between the following :
Fibrous proteins and Globular proteins
Write one difference between α-helix and β-pleated structures of proteins.
Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 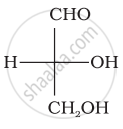 |
| (II) | 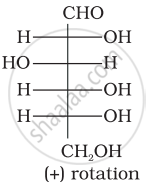 |
| (III) | 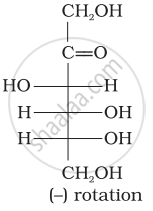 |
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Assertion: β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose,

Reason: Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Explain formation of peptide linkage in protein with an example.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Out of the following, which type of interaction is responsible for the stabilisation of the α-helix structure of proteins?
An α-helix is a structural feature of ______.
Proteins are polymers of ______.
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
β-pleated sheet structure in proteins refers to ______.
