Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are phasors?
उत्तर
A sinusoidal alternating voltage (or current) can be represented by a vector which rotates about the origin in an anti-clockwise direction at a constant angular velocity ω. Such a rotating vector is called a phasor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a series RL circuit, the resistance and inductive reactance are the same. Then the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is
What do you mean by resonant frequency?
Calculate the instantaneous value at 60°, average value and RMS value of an alternating current whose peak value is 20 A.
When does power factor of a series RLC circuit become maximum?
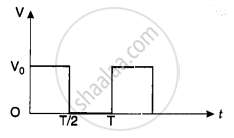
The rms value of potential difference V shown in the figure is ______.
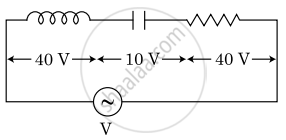
An inductor of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and a resistor of resistance ‘R’ are connected in series to an ac source of potential difference ‘V’ volts as shown in figure. Potential difference across L, C and R is 40 V, 10 V and 40 V, respectively. The amplitude of current flowing through LCR series circuit is `10sqrt2` A. The impedance of the circuit is :
In young's double slit experiment `"d"/"D"`= 10-4 D (d = distance between slits, D = distance of screen from the slits). At a point P on the screen resulting intensity is equal to the intensity due to individual slit l0. Then the distance of point P from the central maximum is (λ = 6000 `"A"^°`)
The r.m.s. value of alternating current is 10 A, having frequency of 50 Hz. The time taken by the current to increase from zero to maximum and the maximum value of current will be ______.
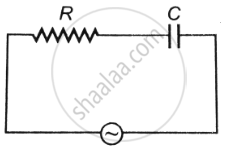
A 50 Hz AC source of 20 volts is connected across R and C as shown in figure. The voltage across R is 12 volt. The voltage across c is ______.