Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are phasors?
Solution
A sinusoidal alternating voltage (or current) can be represented by a vector which rotates about the origin in an anti-clockwise direction at a constant angular velocity ω. Such a rotating vector is called a phasor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a series RL circuit, the resistance and inductive reactance are the same. Then the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is
How will you define RMS value of an alternating current?
What do you mean by resonant frequency?
In any ac circuit, is the applied instantaneous voltage equal to the algebraic sum of the instantaneous voltages across the series elements of the circuit? Is the same true for rms voltage?
The rms current Irms is related to the peak current Io as ______.
The phase relationship between current and voltage in a pure resistive circuit is best represented by ______.
In an alternating current circuit consisting of elements in series, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Which of the following elements are likely to constitute the circuit?
Which of the following is independent of the frequency of a.c?
For a series LCR circuit, I vs ω curve is shown:
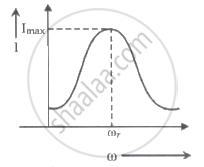
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly capacitive.
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly inductive.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is equal to the resistance of the circuit.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is 0.
A 220V, 50Hz ac source is connected to a coil having coefficient of self-induction of 1H and a resistance of 400 Ω. Calculate:
- the reactance of the coil.
- the impedance of the coil.
- the current flowing through the coil.
