Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the units of heredity.
उत्तर
Genes are the units of heredity which transfer characteristics from parents to their offsprings during reproduction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
"A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed." Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
How did Mendel interpret his results to show that traits may be dominant or recessive? Describe briefly.
List any two contrasting characters other than height that Mendel used in his experiments in pea plants.
With the help of two suitable examples, explain why certain experiences and traits earned by people during their lifetime are not passed on to their next generations. When can such traits be passed on?
What will you get in the F1 and F2 generations in the following cross?
Pure tall pea plant × Pure dwarf pea plant
Gregor Mendel's first law of genetics states "Of a pair of contrasted characters, only one can be represented in a gamete by its internal 'factor Give the modern name for this 'factor'.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) for every hormone there is a gene
(b) for every protein there is a gene
(c) for production of every enzyme there is a gene
(d) for every type of fat there is a gene
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer the following question.
Why are the traits acquired during the life-time-of-an individual not inherited? Explain.
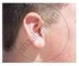
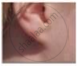
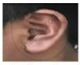
Figures (a) to (d) given below represent the type of ear lobes present in a family consisting of 2 children - Rahul, Nisha and their parents.
|
(a) Rahul's Father |
(b) Rahul |
(c) Rahul's Mother |
(d) Rahul's sister Nisha |
|
(e) |
(f) |
||
| Types of ear lobes | |||
Excited by his observation of different types of ear lobes present in his family, Rahul conducted a survey of the type of ear lobes found {Figure (e) and (f)} in his classmates. He found two types of ear lobes in his classmates as per the frequency given below:
| Sex | Free | Attached |
| Male | 36 | 14 |
| Female | 31 | 19 |
On the basis of the above data answer the following questions.
- Which of the two characteristics - ‘free ear lobe’ or ‘attached ear lobe’ appears to be dominant in this case? Why?
- Is the inheritance of the free ear lobe linked with the sex of the individual? Give a reason for your answer.
- What type of ear lobe is present in father, mother, Rahul and his sister Nisha? Write the genetic constitution of each of these family members which explains the inheritance of this character in this family.
(Gene for the Free ear lobe is represented by F and the gene for the attached ear lobe is represented by f for writing the genetic constitution).
OR
Suresh’s parents have attached ear lobes. What type of ear lobe can be seen in Suresh and his sister Siya? Explain by giving the genetic composition of all.