Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is a lens?
State the condition when a lens is called an equi-convex or equi-concave.
A ray of light incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis, after refraction passes through or appears to come from ______.
In the diagram below, XX’ represents the principal axis, O the optical centre and F the focus of the lens. Complete the path of rays A and B as they emerge out of the lens.
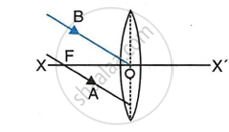 |
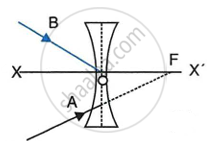 |
| (a) | (b) |
State the condition of the following:
A lens has both its focal lengths equal.
Fig shows an object PQ placed on the principle axis of a lens L. The two foci of the kens are F1 and f2. The image formed by the lens is erect, Virtual and dimnished.
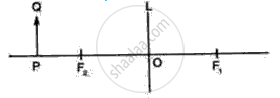
(i) Draw the outline ofthe lens L used and Named it.
(ii) Draw a ray of light starting from Q and passing through O. show the same ray after refraction by the lens.
(iii) Draw another ray from Q Which is incident parallel to the principle axis and show how it emerges after refraction from the lens.
(iv) Locate the final image formed.
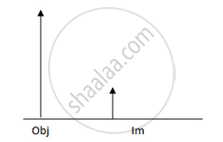
In the following diagram , the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
Complete the following diagram and state what happens to the ray of light after refraction through the lens.
In the following diagram, L1 and L2 are the two convex lense placed at separation equal to the sum of focal lengths of the two lenses. A and B are the two rays of light incident on the lens L1. Complete the path of rays till they emerge out of the lens L2.

What principles have you used in completing the diagram?
