Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to the position of an element in the periodic table when it emits an alpha particle
उत्तर
After emitting an alpha particle the daughter element occupies two places to the left of the parent element in the periodic table.
Reason: If a parent nucleus X becomes a new daughter nucleus Y as a result of -decay, then the -decay can be represented as:
\[\ce{\underset{\text{parent nucleus}}{^A_Z X} ->[Alpha decay] \underset{\text{Daughter nucleus}}{^{A-4}_{z-2}Y} + \underset{\text{α-particle}}{^4_2 He}}\]
Thus, the resulting nucleus has an atomic number equal to (Z-2). Hence, it shifts two places to the left of the parent element in the periodic table.
(b) After emitting a β
-particle, the daughter element occupies one place to the right of the parent element in the periodic table.
Reason: If a parent nucleus X becomes a new daughter nucleus Y as a result of -decay, then the -decay can be represented as:
\[\ce{\underset{\text{parent nucleus}}{^A_Z X} ->[β particle] \underset{\text{Daughter nucleus}}{^{A}_{z+1}Y} + \underset{\text{β-particle}}{^0_-1e}}\]
Thus, the resulting nucleus has an atomic number equal to (Z+1). Hence, it shifts one place to the right of the parent element in the periodic table.
(c) After emitting -radiation, the element occupies the same position in the periodic table.
Reason: If a parent nucleus X becomes a new daughter nucleus Y as a result of -decay, then the -decay can be represented as:
\[\ce{\underset{\text{parent nucleus}}{^A_Z X} ->[γ particle] \underset{\text{Daughter nucleus}}{^{A}_{z}Y} + \underset{\text{γ-particle}}{γ}}\]
Thus, the resulting nucleus has atomic number equal to Z. Hence, it occupies the same position as the parent element in the periodic table.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State three factors on which the rate of emission of electrons from a metal surface depends
Why do Free electrons not leave the metal surface on their own
Arrange α, β, and γ rays in ascending order with respect to their
1) Penetrating power.
2) Ionising power
3) Biological effect
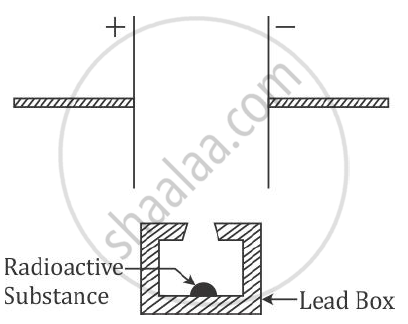
Complete the diagram as given above by drawing the deflection of radioactive radiations in an electric field
What do you mean by Atomic number
A radioactive nucleus `""_"Z"^"A"` X first emits a beta particle and then an alpha particle to give the resulting nucleus `""_"Q"^"P"` Y What will be the values of P and Q in terms of A and Z?
A radioactive substance is oxidized. What changes would you expect to take place in the nature of radioactivity? Explain your answer.
Heavy radioactive elements eventually turn into ______.
If 10% of a radioactive substance decays in every 5 years, then the percentage of the substance that will have decayed in 20 years will be ______.
