Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to the position of an element in the periodic table when it emits an alpha particle
उत्तर
After emitting an alpha particle the daughter element occupies two places to the left of the parent element in the periodic table.
Reason: If a parent nucleus X becomes a new daughter nucleus Y as a result of -decay, then the -decay can be represented as:
\[\ce{\underset{\text{parent nucleus}}{^A_Z X} ->[Alpha decay] \underset{\text{Daughter nucleus}}{^{A-4}_{z-2}Y} + \underset{\text{α-particle}}{^4_2 He}}\]
Thus, the resulting nucleus has an atomic number equal to (Z-2). Hence, it shifts two places to the left of the parent element in the periodic table.
(b) After emitting a β
-particle, the daughter element occupies one place to the right of the parent element in the periodic table.
Reason: If a parent nucleus X becomes a new daughter nucleus Y as a result of -decay, then the -decay can be represented as:
\[\ce{\underset{\text{parent nucleus}}{^A_Z X} ->[β particle] \underset{\text{Daughter nucleus}}{^{A}_{z+1}Y} + \underset{\text{β-particle}}{^0_-1e}}\]
Thus, the resulting nucleus has an atomic number equal to (Z+1). Hence, it shifts one place to the right of the parent element in the periodic table.
(c) After emitting -radiation, the element occupies the same position in the periodic table.
Reason: If a parent nucleus X becomes a new daughter nucleus Y as a result of -decay, then the -decay can be represented as:
\[\ce{\underset{\text{parent nucleus}}{^A_Z X} ->[γ particle] \underset{\text{Daughter nucleus}}{^{A}_{z}Y} + \underset{\text{γ-particle}}{γ}}\]
Thus, the resulting nucleus has atomic number equal to Z. Hence, it occupies the same position as the parent element in the periodic table.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When does the nucleus of an atom tend to become radioactive?
Answer the following questions based on a hot cathode ray tube.
What will happen to the beam when it passes through the electric field?
State three factors on which the rate of emission of electrons from a metal surface depends
Write one use of cathode ray tube.
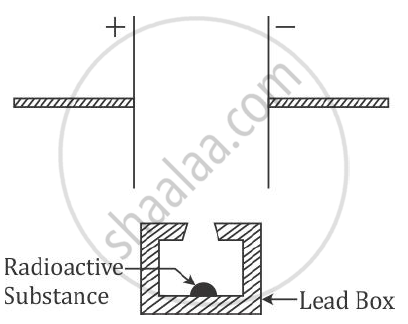
Complete the diagram as given above by drawing the deflection of radioactive radiations in an electric field
Explain the use of radioactive in the field of medicine, agriculture and industry.
A certain nucleus A (mass number 238 and atomic number 92) is radioactive and becomes a nucleus B (mass number 234 and atomic number 90) by the loss of one particle.
What particle was emitted?
What are the types of emission?
Why are materials of low work function preferred as thermionic cathode materials?
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 100 hours. The fraction of original activity that will remain after 150 hours would be ______.
