Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is an LED? Give the principle of its operation with a diagram.
उत्तर
1. LED is a p-n junction diode which emit visible or invisible light when it is forward bias.
2. It converts electrical energy to light energy.
3. It consists of p-layer, n-layer and substrate. External resistance in series with biasing source is required to limit forward current through LED. It has anode and cathode.
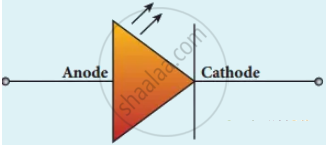
Circuit symbol of LED
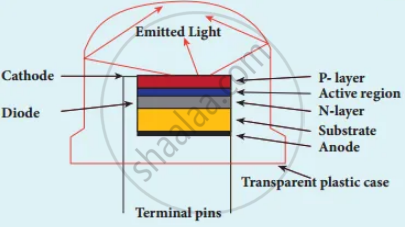
Inside view of LED

Schematic diagram to explain recombination process
4. When a p-n junction is forward bias, conduction band electron on n-side and valence band hole on p side diffuse across the junction.
5. When they cross junction, they become excess minority carriers. These excess minority carriers recombine with oppositely charged majority carriers in the respective region.
6. During the recombination process energy is released is the form of light or heat.
7. The colour of the light is determined by the energy band gap of the material.
8. LED’s with wide range colours such as blue (Sic), green (AlGaP), red(GaAsP), white(GaInN) is also available.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The barrier potential of a silicon diode is approximately, ____________.
In an unbiased p-n junction, the majority of charge carriers (that is, holes) in the p-region diffuse into the n-region because of
If a positive half-wave rectified voltage is fed to a load resistor, for which part of a cycle there will be current flow through the load?
The zener diode is primarily used as ____________.
The barrier potential of a p-n junction depends on
(i) type of semiconductor material
(ii) amount of doping
(iii) temperature
Which one of the following is correct?
Which one of the following represents forward bias diode?
Distinguish between avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown.
Write a short note on diffusion current across the p-n junction.
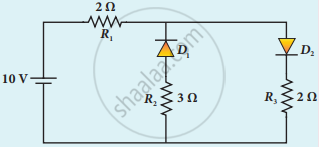
The given circuit has two ideal diodes connected as shown in the figure below. Calculate the current flowing through the resistance R1.
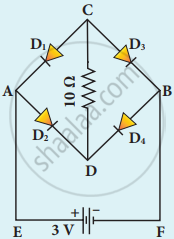
Four silicon diodes and a 10 Ω resistor are connected as shown in the figure below. Each diode has a resistance of 1 Ω. Find the current flows through the 10 Ω resistor.