Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is monosaccharide?
उत्तर
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates which do not hydrolyse further into smaller units of polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
acetic anhydride
Explain D and L configuration in sugars.
Draw the structure of the pyran.
By which of the following process formation of glycosidic bond occurs?
From the following identify an example of disaccharides.
Which of the following is the basic unit of carbohydrates?
From the following identify the group that is exclusively consists of polysaccharides.
Identify the sugar having the molecular formula C6H1206.
By which of the following feature we can identify the relatively small DNA molecules of plasmids?
____________ do not give smaller sugar units on hydrolysis.
4-O-(α-D-Glucopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranose is ____________.
Which one of the following carbohydrates is insoluble in water?
Which one of the following sugar does NOT have same empirical fonnula as that of carbohydrate?
What is the number of hydroxyl groups present in lactic acid?
Identify the number of secondary carbon atoms in glucose.
On hydrolysis sucrose gives ____________.
Identify the number of oxygen atoms present in saccharic acid?
What is the product obtained when Br2 water reacts with glucose?
Which among the following observations suggests that glucose also exists in cyclic form?
Assertion: A solution of sucrose in water is dextrorotatory. But on hydrolysis in the presence of little hydrochloric acid, it becomes levorotatory.
Reason: Sucrose hydrolysis gives equal amounts of glucose and fructose. As a result of this change in sign of rotation is observed.
Complete hydrolysis of cellulose gives ____________.
The molecule of glucose is also called ______.
Which carbon atoms of fructose are bonded together through oxygen forming fructofuranose?
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
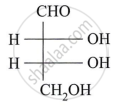
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
dil. Nitric acid.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
