Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain D and L configuration in sugars.
उत्तर
D and L configuration in sugars:
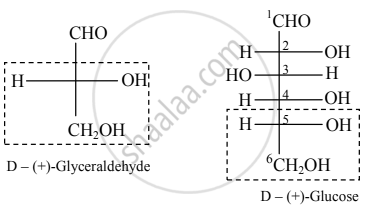
- Conventionally (+)-glyceraldehyde is represented by the Fischer projection formula having –OH group attached to C-2 on the right side and this configuration is denoted by symbol ‘D’.
- Similarly, the configuration of (–) glyceraldehyde is denoted by the symbol ‘L’.
- All the compounds which can be correlated by a series of chemical reactions to (+)-glyceraldehyde are said to have D-configuration.
- And compounds which are chemically correlated to (–)-glyceraldehyde are said to have L-configuration. This is the system of the relative configuration of chiral compounds.
- A monosaccharide is assigned D/L configuration on the basis of the configuration of the lowest chiral carbon in its Fischer projection formula.
- Relative configuration of (+)-glucose with respect to (+)-glyceraldehyde can be drawn as follows:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give two evidences for presence of formyl group in glucose.
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of glucopyranose.
Glucose on oxidation with dilute nitric acid gives _______________
The glycosidic linkage in maltose is formed between _______________
Identify the given structure 'P' and 'Q'.
From the following identify an example of disaccharides.
Which of the following monosaccharides is a tetrose sugar?
Carbohydrates can contain which of the following chemical groups?
Fructose is the fruit sugar and chemically it is ketohexose but it has a ______ rather than a ______.
Which among the following compounds is obtained when glucose reacts with hydrogen cyanide?
From the following identify the two types of glucose polymers present in starch.
Which carbon atoms of α- D glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose respectively are linked together to form glycosidic linkage in sucrose?
Raffinose, sucrose and stachyose are respectively ____________.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding glucose.
Which one of the following is Tetrose sugar?
Which among the following statements is true for amylose?
What is the molecular formula of glyceraldehyde?
Which among the following is a product of hydrolysis of one mole raffinose?
How many optical isomers are possible for a compound having four asymmetric carbon atoms?
The number of sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon in fructose are respectively ____________.
What are reducing and non-reducing sugars?
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Starch
Glucose on oxidation with bromine water yields gluconic acid. This reaction confirms the presence of ______.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
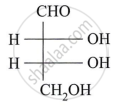
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
Carbohydrates that do not undergo hydrolysis further are called ______.
Explain the hydrolysis of sucrose.
The linkage present in Lactose is ______.
