Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain D and L configuration in sugars.
उत्तर
D and L configuration in sugars:
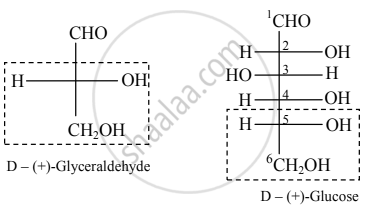
- Conventionally (+)-glyceraldehyde is represented by the Fischer projection formula having –OH group attached to C-2 on the right side and this configuration is denoted by symbol ‘D’.
- Similarly, the configuration of (–) glyceraldehyde is denoted by the symbol ‘L’.
- All the compounds which can be correlated by a series of chemical reactions to (+)-glyceraldehyde are said to have D-configuration.
- And compounds which are chemically correlated to (–)-glyceraldehyde are said to have L-configuration. This is the system of the relative configuration of chiral compounds.
- A monosaccharide is assigned D/L configuration on the basis of the configuration of the lowest chiral carbon in its Fischer projection formula.
- Relative configuration of (+)-glucose with respect to (+)-glyceraldehyde can be drawn as follows:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give scientific reasons:
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
Explain the classification of carbohydrates with examples.
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
hydroxylamine
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
hydrogen iodide
Write a chemical reaction to convert glucose into glucose cyanohydrin.
Which of the following monosaccharides is a tetrose sugar?
From the following identify the materials that are made up of cellulose.
i. Plant cell wall
ii. Exoskeleton of arthropods
iii. Paper from plant pulp
iv. Cotton fibre
4-O-(α-D-Glucopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranose is ____________.
The general formula for polysaccharide is ____________.
Which one of the following carbohydrates is insoluble in water?
Which one of the following is NOT soluble in water?
Glucose and gluconic acid treated with dilute nitric acid forms saccharic acid. What does this indicate?
When one mole of lactose is hydrolysed, the hydrolysate contains ____________.
Which one given below is a non-reducing sugar?
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Sucrose
Lactose is made of ______.
A molecule of stachyose contains how many carbon atoms?
The two monosaccharides in a disaccharide are held together by ______ bonds.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called ______.
Starch and cellulose are compounds made up of many units of ______.
Formation of gluconic acid from glucose by oxidation using Br2 water.
Consider the following reaction
\[\ce{A <-[Br2 - H2O] Glucose ->[HNO3] B}\]
Here, 'A' and 'B' are respectively.
The glycosidic linkage present in maltose is ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
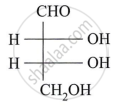
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
Bromine water
Write the ring structure of glucose.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
