Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain D and L configuration in sugars.
Solution
D and L configuration in sugars:
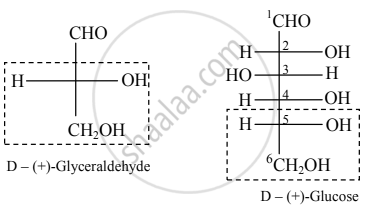
- Conventionally (+)-glyceraldehyde is represented by the Fischer projection formula having –OH group attached to C-2 on the right side and this configuration is denoted by symbol ‘D’.
- Similarly, the configuration of (–) glyceraldehyde is denoted by the symbol ‘L’.
- All the compounds which can be correlated by a series of chemical reactions to (+)-glyceraldehyde are said to have D-configuration.
- And compounds which are chemically correlated to (–)-glyceraldehyde are said to have L-configuration. This is the system of the relative configuration of chiral compounds.
- A monosaccharide is assigned D/L configuration on the basis of the configuration of the lowest chiral carbon in its Fischer projection formula.
- Relative configuration of (+)-glucose with respect to (+)-glyceraldehyde can be drawn as follows:
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give scientific reasons:
The disaccharide sucrose gives negative Tollens test while the disaccharide maltose gives a positive Tollens test.
Give scientific reasons:
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of glucopyranose.
Write the name of the polysaccharide used for the commercial preparation of glucose.
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
acetic anhydride
What is monosaccharide?
Identify the substances having glycosidic bond and peptide bond, respectively in their structure:
From the following identify the group that is exclusively consists of polysaccharides.
Identify a non-reducing carbohydrate from the following.
Match the columns and select the correct option.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | Starch | a. | Animal storage molecule |
| ii. | Cellulose | b. | Plant storage molecule |
| iii. | Glycogen | c. | Heparin |
| iv. | Heteropolysaccharide | d. | Plant cell wall component |
Which reagent among the following is used to confirm presence of aldehydic carbonyl group in glucose?
All these carbohydrates contain \[\ce{1 -> 4β}\] glycosidic linkage, EXCEPT ____________.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding glucose.
Which one of the following is an oligosaccharide?
Which of the following statements is NOT true for glyceraldehyde?
Which one of the following sugar does NOT have same empirical fonnula as that of carbohydrate?
What is the product obtained when Br2 water reacts with glucose?
The correct corresponding order of names of four aldoses with configuration given below Respectively is:
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(HCN)] Product ->[(hydrolysis)] Product ->[(HI + Heat)] A}\], the compound A is:
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Maltose
Lactose is made of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
CH2 OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2 OH is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
