Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
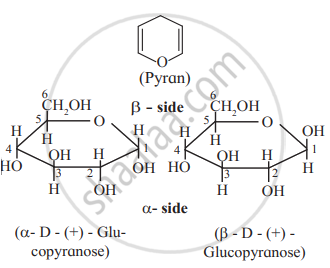
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of glucopyranose.
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
Give scientific reasons:
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
Draw the structure of α-D glucopyranose.
Write the name of the unit to which glucose unit is linked to from sucrose.
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
acetic anhydride
Write a commercial method for preparation of glucose.
What is monosaccharide?
Carbohydrates can contain which of the following chemical groups?
Identify the sugar having the molecular formula C6H1206.
From the following identify the materials that are made up of cellulose.
i. Plant cell wall
ii. Exoskeleton of arthropods
iii. Paper from plant pulp
iv. Cotton fibre
The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in the glucose molecule is ____________.
Prolonged heating of glucose with hot HI results in the formation of ____________.
Which of the following monosaccharide is a ketohexose?
Which one of the following is a carbohydrate but does NOT follow the general formula of carbohydrate?
Which one of the following is generally applicable to polysaccharides?
Which of the following statements is NOT true for glyceraldehyde?
When 2 moles of stachyose is hydrolyzed, the number of moles of galactose obtained is ____________.
On hydrolysis sucrose gives ____________.
What is the product obtained when Br2 water reacts with glucose?
When one mole of lactose is hydrolysed, the hydrolysate contains ____________.
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(HCN)] Product ->[(hydrolysis)] Product ->[(HI + Heat)] A}\], the compound A is:
Assertion: A solution of sucrose in water is dextrorotatory. But on hydrolysis in the presence of little hydrochloric acid, it becomes levorotatory.
Reason: Sucrose hydrolysis gives equal amounts of glucose and fructose. As a result of this change in sign of rotation is observed.
α-D (+) Glucose and β-D (+) glucose are ____________.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Which one is a non-reducing commercial sugar?
Identify the product obtained in the following conversion.
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(O)][Br2 water] Product}\]
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
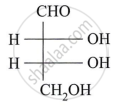
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
dil. Nitric acid.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
