Advertisements
Advertisements
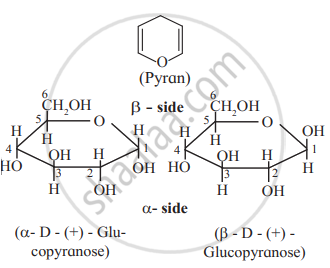
प्रश्न
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of glucopyranose.
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of maltose
Glucose on oxidation with dilute nitric acid gives _______________
Write the name of the polysaccharide used for the commercial preparation of glucose.
Write chemical reaction for following conversions
glucose into gluconic acid
Write a chemical reaction to convert glucose into glucose cyanohydrin.
By which of the following process formation of glycosidic bond occurs?
By which of the following feature we can identify the relatively small DNA molecules of plasmids?
Identify a non-reducing carbohydrate from the following.
Raffinose, sucrose and stachyose are respectively ____________.
The general formula for polysaccharide is ____________.
Which one of the following is generally applicable to polysaccharides?
Which one of the following carbohydrates is insoluble in water?
Which among the following reagents is used to confirm the presence of carbonyl group in glucose?
Identify the number of oxygen atoms present in saccharic acid?
What is the product obtained when Br2 water reacts with glucose?
Assertion: A solution of sucrose in water is dextrorotatory. But on hydrolysis in the presence of little hydrochloric acid, it becomes levorotatory.
Reason: Sucrose hydrolysis gives equal amounts of glucose and fructose. As a result of this change in sign of rotation is observed.
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Maltose
If 'n' represents total number of asymmetric carbon atoms in a compound, then the possible· number of optical isomers of the compound is ______.
Lactose is made of ______.
A molecule of stachyose contains how many carbon atoms?
The glycosidic linkage present in maltose is ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
dil. Nitric acid.
Explain the hydrolysis of sucrose.
CH2 OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2 OH is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
Write the Zwitter ion structure of alanine.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
