Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
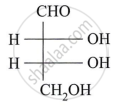
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of maltose
Solution

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give scientific reasons:
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
The glycosidic linkage in maltose is formed between _______________
Draw the structure of α-D glucopyranose.
Explain the classification of carbohydrates with examples.
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
acetic anhydride
From the following which is a heteropolysaccharide?
Identify the WRONG statement.
By which of the following feature we can identify the relatively small DNA molecules of plasmids?
Chitin is a/an ______.
All these carbohydrates contain \[\ce{1 -> 4β}\] glycosidic linkage, EXCEPT ____________.
Which of the following monosaccharide is a ketohexose?
Which one of the following is a carbohydrate but does NOT follow the general formula of carbohydrate?
Which among the following reagents is used for conversion of glucose to glucoxime?
Which among the following reagents is used to obtain gluconic acid from glucose?
How many hydroxyl groups are present in Erythrulose?
Assertion: A solution of sucrose in water is dextrorotatory. But on hydrolysis in the presence of little hydrochloric acid, it becomes levorotatory.
Reason: Sucrose hydrolysis gives equal amounts of glucose and fructose. As a result of this change in sign of rotation is observed.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Sucrose
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called ______.
Identify the product obtained in the following conversion.
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(O)][Br2 water] Product}\]
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
CH2 OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2 OH is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
