Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a neat diagram for the following:
Haworth formula of maltose
उत्तर

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Glucose on oxidation with dilute nitric acid gives _______________
Write chemical reaction for following conversions
glucose into glucoxime
Explain the classification of carbohydrates with examples.
Which of the following type of carbohydrates cannot be hydrolyzed?
From the following identify an example of disaccharides.
Formation of lactose by conden ation results in the release of how many molecules of water?
By which of the following feature we can identify the relatively small DNA molecules of plasmids?
Identify a non-reducing carbohydrate from the following.
____________ do not give smaller sugar units on hydrolysis.
Which among the following type of linkages is present in cellulose?
Raffinose, sucrose and stachyose are respectively ____________.
Prolonged heating of glucose with hot HI results in the formation of ____________.
Which element among the following is not present in saccharine?
Stachyose is ____________.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - Br ->[Na][dry ether] A ->[Cl2] B}\]
Identify the product B in the above reaction.
On hydrolysis sucrose gives ____________.
Identify the product Y in the following reaction.
\[\ce{Maltose ->[Hydrolysis] X ->[dil. HNO3][(excess)] Y}\]
Which among the following is a product of hydrolysis of one mole raffinose?
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(HCN)] Product ->[(hydrolysis)] Product ->[(HI + Heat)] A}\], the compound A is:
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Maltose
Write the structure of α-D (+) glucopyranose.
Match the Column I with Column II and choose the correct answer from options below:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Purine | 1. Glycogen |
| B. Pyrimidine | 2. Cellulose |
| C. Structural polysaccharide | 3. Glucagon |
| D. Storage polysaccharide | 4. Adenine |
| 5. Cytosine |
Consider the following reaction
\[\ce{A <-[Br2 - H2O] Glucose ->[HNO3] B}\]
Here, 'A' and 'B' are respectively.
The glycosidic linkage present in maltose is ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
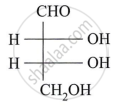
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2 OH}\] is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
