Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH]4]– only whereas AlCl3 in acidified aqueous solution forms [Al(H2O)6]3+ ion. Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
उत्तर
\[\ce{BCl3 + 3H2O -> B(OH)3 + 3HCl}\]
\[\ce{B(OH)3 + H2O -> [B(OH)4]– + H+}\]
B(OH)3 due to its incomplete octet accepts an electron pair (as OH–) to give [B(OH)4]–. Boron in this ion involves one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals. Thus, hybridisation of B in [B(OH)4]– is sp3.
\[\ce{AlCl3 + 6H2O ->[HCl] [Al(H2O)6]^{3+} + 3Cl-}\]
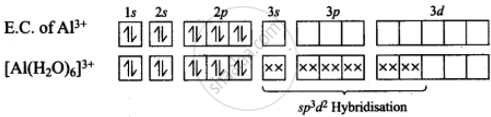
Hence, hybridisation of Al is sp3d2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If B–Cl bond has a dipole moment, explain why BCl3 molecule has zero dipole moment.
Suggest reasons why the B–F bond lengths in BF3 (130 pm) and `"BF"_4^(-)` (143 pm) differ.
Ionisation enthalpy (∆iH1kJ mol–1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
The most commonly used reducing agent is ______.
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
BCl3
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions:
\[\ce{X ->[Δ][370 K] HBO2 ->[Δ][> 370 K] Z}\]
Complete the following chemical equations:
\[\ce{Z + 3 LiAlH4 -> X + 3LiF + 3AlF_3}\]
\[\ce{X + 6H2 -> Y + 6H2}\]
\[\ce{3X + 3O2 ->[Δ] B2O3 + 3H2O}\]
Match the species given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{BF^{-}4}\] | (a) Oxidation state of central atom is +4 |
| (ii) AICI3 | (b) Strong oxidising agent |
| (iii) SnO | (c) Lewis acid |
| (iv) PbO2 | (d) Can be further oxidised |
| (e) Tetrahedral shape |
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Atomic size
Which one of the following is the correct statement?
