Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH]4]– only whereas AlCl3 in acidified aqueous solution forms [Al(H2O)6]3+ ion. Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
Solution
\[\ce{BCl3 + 3H2O -> B(OH)3 + 3HCl}\]
\[\ce{B(OH)3 + H2O -> [B(OH)4]– + H+}\]
B(OH)3 due to its incomplete octet accepts an electron pair (as OH–) to give [B(OH)4]–. Boron in this ion involves one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals. Thus, hybridisation of B in [B(OH)4]– is sp3.
\[\ce{AlCl3 + 6H2O ->[HCl] [Al(H2O)6]^{3+} + 3Cl-}\]
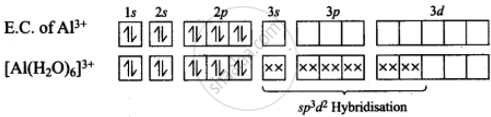
Hence, hybridisation of Al is sp3d2.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Aluminium trifluoride is insoluble in anhydrous HF but dissolves on the addition of NaF. Aluminium trifluoride precipitates out of the resulting solution when gaseous BF3 is bubbled through. Give reasons.
In some of the reactions thallium resembles aluminium, whereas in others it resembles with group I metals. Support this statement by giving some evidences.
Ionisation enthalpy (∆iH1kJ mol–1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
Dry ice is ______.
Cement, the important building material is a mixture of oxides of several elements. Besides calcium, iron and sulphur, oxides of elements of which of the group (s) are present in the mixture?
Which of the following statements are correct. Answer on the basis of Figure.

(i) The two birdged hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane;
(ii) Out of six B – H bonds two bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2-electron bonds.
(iii) Out of six B – H bonds four B – H bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2 electron bonds;
(iv) The four-terminal B – H bonds are two centre-two electron regular bonds.
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
BCl3
Explain the following:
Electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative as compared to fluorine.
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Nature of halides
A group 13 element ‘X’ reacts with chlorine gas to produce a compound XCl3. XCl3 is electron deficient and easily reacts with NH3 to form \[\ce{Cl3X –> NH3}\] adduct; however, XCl3 does not dimerize X is ______.
