Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH]4]– only whereas AlCl3 in acidified aqueous solution forms [Al(H2O)6]3+ ion. Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
उत्तर
\[\ce{BCl3 + 3H2O -> B(OH)3 + 3HCl}\]
\[\ce{B(OH)3 + H2O -> [B(OH)4]– + H+}\]
B(OH)3 due to its incomplete octet accepts an electron pair (as OH–) to give [B(OH)4]–. Boron in this ion involves one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals. Thus, hybridisation of B in [B(OH)4]– is sp3.
\[\ce{AlCl3 + 6H2O ->[HCl] [Al(H2O)6]^{3+} + 3Cl-}\]
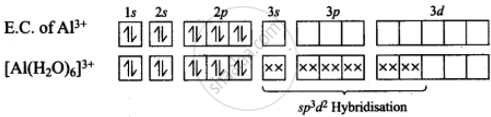
Hence, hybridisation of Al is sp3d2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when BF3 is reacted with ammonia?
In some of the reactions thallium resembles aluminium, whereas in others it resembles with group I metals. Support this statement by giving some evidences.
Which of the following oxides is acidic in nature?
Ionisation enthalpy (∆iH1kJ mol–1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
BCl3
Explain the following:
Boron does not exist as B3+ ion.
Explain the following:
Tl (NO3)3 acts as an oxidising agent.
Three pairs of compounds are given below. Identify that compound in each of the pairs which has group 13 element in more stable oxidation state. Give reason for your choice. State the nature of bonding also.
AlCl3 , AlCl
BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised through halogen bridging. Give reason. Explain the structure of the dimer of AlCl3 also.
Which one of the following is the correct statement?
