Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a ray diagram, state what is meant by refraction of light. State Snell’s law for refraction of light and also express it mathematically.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is 2/3 and the refractive index of water with respect to air is 4/3. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s, find the speed of light in (a) air, (b) water.
उत्तर
When a ray of light travels from one transparent medium to another, it bends at the surface. This happens because different media have different optical densities.
The phenomenon of bending of light as it travels from one medium to another is known as refraction of light.
As a ray of light moves from an optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium, it bends towards the normal at the point of incidence. Therefore, the angle of incidence (i) is greater than the angle of refraction (r). Hence, i > r
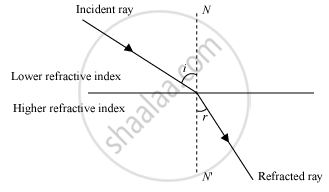
The first law of refraction is also known as Snell’s law.
Snell’s law: The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant. This is known as Snell’s law. Mathematically, it can be given as follows:
`sini/sinr="constant"=`\[^aμ_b\]
\[^gμ_a\] `=2/3=μ_a/μ_g`
\[^aμ_w\]`=4/3=μ_w/μ_a`
Vg = 2 × 108 m/s
Now we know μ=`C/V`
Where µ is absolute refractive index of a medium w.r.t. vacuum
C is speed of light in vacuum
V is speed of light in medium.
(a) Now `μ_a=C/V`
`μ_g=C/V_g`
Dividing `μ_a/μ_g=V_g/V_a=2/3`
`V_a=3/2xxV_g=3/2xx2xx10^8` m/s
`=3xx10^8`m/s
(b) Again `μ_w=C/V_w`
`μ_a=C/V_a`
Dividing `μ_w/μ_a=V_a/V_w=4/3`
`V_w=3/4xx3xx10^8`
`=9/4xx10^8`
= 2.25 x 108 m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The velocity of light in a medium is 1.5 x 108 m/s. What is the refractive index of the medium with respect to air, if the velocity in air is 3 x 108 m/s?
A ray of light travelling in air goes into water. The angle of refraction will be:
(a) 90°
(b) smaller than the angle of incidence
(c) equal to the angle of incidence
(d) greater than the angle of incidence
A ray of light travelling in water falls at right angles to the boundary of a parallel-sided glass block. The ray of light:
(a) is refracted towards the normal
(b) is refracted away from the normal
(c) does not get refracted
(d) is reflected along the same path
State and explain the laws of refraction of light with the help of a labelled diagram.
Light travels through air at 300 million ms−1. On entering water it slows down to 225 million ms−1. Calculate the refractive index of water.
The refractive index of water is:
(a) 1.33
(b) 1.50
(c) 2.42
(d) 1.36
Name a liquid whose mass density is less than that of water but it is optically denser than water.
Light travels with a velocity 1.5 x 108 m/s in a medium. On entering second medium its velocity becomes 0.75 x 108 m/s. What is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium?
Solve the following example.
Speed in first medium, v1 = 3 × 108 m/s
Speed in second medium, v2 = 2 × 108 m/s
Then 2n1 = ?
Define the refractive index of a medium.
