Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
उत्तर १

Logistic growth curve of population
- Resources like food and space are not always unlimited. They may be plenty in the beginning; but as the population density increases, competition for those resources starts, resulting in a slowdown in the rate at which the original population was growing. This results in a logistic or sigmoid growth curve.
- Competition between individuals for limited resources will weed out the ‘weaker' ones. Only the ‘fittest’ individuals will survive and reproduce.
- A given habitat has enough resources to support a maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. This limit can be called nature’s carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat.
- A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows initially a lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration, and finally an asymptote when the population density reaches the carrying capacity.
- A plot of population density (N) in relation to time (t) results in a sigmoid curve. This type of population growth is called VerhulstPearl Logistic Growth.
- Since resources for the growth of most animal populations, are finite and become limiting sooner or later, the logistic growth model is considered a more realistic one.
उत्तर २
In nature, No population of any species in nature has at its disposal unlimited resources to permit exponential growth. This leads to competition between individuals for limited resources. Eventually, the ‘fittest’ individual will survive and reproduce. In nature, a given habitat has enough resources to support the maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. Let us call this limit nature’s carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat.
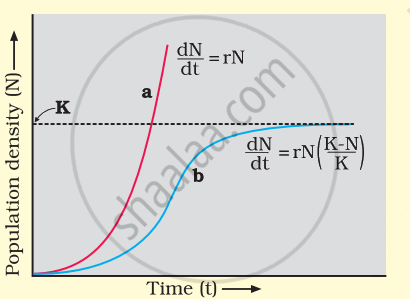
A population growing in a habitat with limited resources initially shows a lag phase. This is followed by acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote phase. Population density feeding capacity type of population growth is called Verhulst-Pearl Logistic Growth. The following equation represents it –
`(dN)/(dt) = rN ((K - N)/K) = rN (1 - N/K)`
where `(dN)/(dt)` = rate of change in population size
where N = population density at time t,
r = rate of natural increase,
K = feeding capacity
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the role of VAM related to soil fertility.
What is mutualism?
Apart from being a part of the food chain, predators play other important roles. Mention any two such roles supported by examples.
Competition and Mutualism.
Select the statement which explains the best parasitism.
Give one example of Interspecific competition.
Give one example for Mutualism
Define the following term:
Camouflage
Community is defined as ______.
The cattle egret and grazing cattle in close association is a classic example of ______.
What is Commensalism? Explain it with suitable example.
Two species competing for the same resources, avoid competition by choosing different times for feeding, also known as ______
Select the CORRECT match:
| I | II | ||
| i. | Competition | a. | Lichen |
| ii. | Commensalism | b. | Sea anemone and clownfish |
| iii. | Mutualism | c. | Lions and Leopards |
What are the organisms that feed on plant sap and other plant parts called?
In an association of two animal species, one is a termite which feeds on wood and the other is a protozoan Trichonympha present in the gut of the termite. What type of association they establish?
While living in and on the host species, the animal parasite has evolved certain adaptations. Describe these adaptations with examples.
Interaction between clown fish living among the stinging tentacles of sea anemone is an example of ______.
"Abingdon tortoise in Galapagos islands became extinct within a decade on introduction of goats in the island." Explain giving reason.
What are the special adaptations that endoparasites show?
Select the statement which best describes parasitism.
