Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
उत्तर १

Logistic growth curve of population
- Resources like food and space are not always unlimited. They may be plenty in the beginning; but as the population density increases, competition for those resources starts, resulting in a slowdown in the rate at which the original population was growing. This results in a logistic or sigmoid growth curve.
- Competition between individuals for limited resources will weed out the ‘weaker' ones. Only the ‘fittest’ individuals will survive and reproduce.
- A given habitat has enough resources to support a maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. This limit can be called nature’s carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat.
- A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows initially a lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration, and finally an asymptote when the population density reaches the carrying capacity.
- A plot of population density (N) in relation to time (t) results in a sigmoid curve. This type of population growth is called VerhulstPearl Logistic Growth.
- Since resources for the growth of most animal populations, are finite and become limiting sooner or later, the logistic growth model is considered a more realistic one.
उत्तर २
In nature, No population of any species in nature has at its disposal unlimited resources to permit exponential growth. This leads to competition between individuals for limited resources. Eventually, the ‘fittest’ individual will survive and reproduce. In nature, a given habitat has enough resources to support the maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. Let us call this limit nature’s carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat.
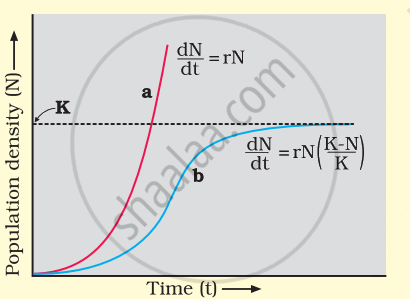
A population growing in a habitat with limited resources initially shows a lag phase. This is followed by acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote phase. Population density feeding capacity type of population growth is called Verhulst-Pearl Logistic Growth. The following equation represents it –
`(dN)/(dt) = rN ((K - N)/K) = rN (1 - N/K)`
where `(dN)/(dt)` = rate of change in population size
where N = population density at time t,
r = rate of natural increase,
K = feeding capacity
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which day is observed as ‘World Environment Day’?
Define the following term:
Commensalism
Name the type of association: Crow feeding the hatchling of Koel
What is the ecological process behind the biological control method of managing pest insects?
In Logistic growth curve lag phase shows______.
What is Mortality? What are its two types?
Define mutualism.
Define population growth. Explain different types of age pyramids.
Statement I: If one or two species are lost, it may not affect proper functioning of ecosystem.
Statement II: Loss of key species causes serious threat to functioning of ecosystem. Choose the correct alternative with reference to the above statements
The correct description for the interspecific interaction shown in the given figure is ______

Identify the type of negative interaction.
Which one of the following is NOT an example of mutualism?
The presence or interference of one species leads to reduction in feeding efficiency of other species is termed as
What is the interaction between two species called?
Give one example for the following type.
Phytophagous animal
Give one example for the following type.
Chemical defense agent
Give one example for the following:
A parasitic angiosperm
Write the observations made at the end of Connell's field, experiment on barnacles on the rocky sea coasts of Scotland.
What are the special adaptations that endoparasites show?
