Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
\[\ce{Λ^0_m H2O}\] is equal to:
(i) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaCl)}}}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)}}}}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Λ^0_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)}}}}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4OH)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4Cl)}}}}\]
उत्तर
(i) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaCl)}}}}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4OH)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4Cl)}}}}\]
Explanation:
\[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(H_2O)} = \ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaCl)}}}}}\]
\[\ce{Λ^0_{m(H^+)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(OH^-)} = \ce{Λ^0_{m(H^+)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(Cl^-)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(Na^+)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(OH^-)} - \ce{Λ^0_{m(Na^+)} - \ce{Λ^0_{m(Cl^-)}}}}}}}}}\]
\[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)} = \ce{Λ^0_m_{(H_2O)}}}}}\]
\[\ce{Λ^0_{m(H^+)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(NO_3^-)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(Na^+)} - \ce{Λ^0_{m(OH^-)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(Na^+)} + \ce{Λ^0_{m(NO_3^-)} = \ce{Λ^0_{m(H^+)} - \ce{Λ^0_{m(OH^-)}}}}}}}}}\]
\[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4OH)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4Cl)} = \ce{Λ^0_m_{(H_2O)}}}}}\]
However, the sum of molar conductivities of constituent ions gives the molar conductivity of water but here \[\ce{NH4OH}\] is a weak electrolyte of which complete decomposition is not possible.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution. [Given: Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m-1 .]
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions states ____________.
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on:
(i) temperature.
(ii) distance between electrodes.
(iii) concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) surface area of electrodes.
Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below:
`E_("F"_2//"F"^-)^Θ` = 2.87 V, `"E"_(("Li"^(+))//("Li"^-))^Θ` = − 3.5V, `"E"_(("Au"^(3+))//("Au"))^Θ` = 1.4 V, `"E"_(("Br"_(2))//("Br"^-))^Θ` = 1.09 V
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) F2 | (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent |
| (ii) Li | (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidising agent |
| (iii) Au3+ | (c) non metal which is the best oxidising agent |
| (iv) Br– | (d) unreactive metal |
| (v) Au | (e) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+ |
| (vi) Li+ | (f) anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
| (vii) F– | (g) metal ion which is an oxidising agent |
Which of the following increases with the increase in the concentration of the solution?
The molar conductivity of 0.007 M acetic acid is 20 S cm2 mol−1. What is the dissociation constant of acetic acid? Choose the correct option.
`[(Λ_("H"^+)^ο = 350 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1), (Λ_("CH"_3"COO"^-)^ο = 50 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1)]`
The molar conductance of NaCl, HCl, and CH3COONa at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16, and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
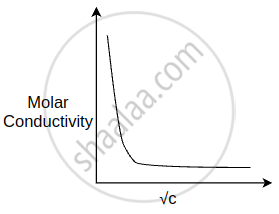
The electrolyte X is ______.
The specific conductance of 2.5 × 10-4 M formic acid is 5.25 × 10-5 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given `λ°_("H"^+)` = 349.5 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 and
`λ°_("HCOO"^-) = 50.5 " ohm"^-1 "cm"^2 "mol"^-1`
