Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date: मार्च 2023
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions :
- There are 35 questions in all. All questions are compulsory
- This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D, and Section E. All the sections are compulsory.
- Section A contains eighteen MCQs of 1 mark each, Section B contains seven questions of two marks each, Section C contains five questions of three marks each, Section D contains three long questions of five marks each, and Section E contains two case study-based questions of 4 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in sections B, C, D, and E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- Use of calculators is not allowed.
According to Coulomb's law, which is the correct relation for the following figure?

q1q2 > 0
q1q2 < 0
q1q2 = 0
1 > q1/q2 > 0
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
The electric potential on the axis of an electric dipole at a distance ‘r from it’s centre is V. Then the potential at a point at the same distance on its equatorial line will be ______.
2V
-V
V/2
Zero
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
The temperature (T) dependence of resistivity of materials A and material B is represented by fig (i) and fig (ii) respectively. Identify material A and material B.
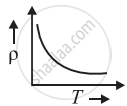 fig. (i) |
 fig. (ii) |
material A is copper and material B is germanium
material A is germanium and material B is copper
material A is nichrome and material B is germanium
material A is copper and material B is nichrome
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio 2:3. Loop Q carries a current 9 A in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry ______.
3 A in clockwise direction
9 A in clockwise direction
6 A in anti-clockwise direction
6 A in the clockwise direction
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A long straight wire of circular cross section of radius 'a' carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed across its cross section. The ratio of magnitudes of the magnetic field at a point `a/2` above the surface of wire to that of a point `a/2` below its surface is ______.
4 : 1
1 : 1
4 : 3
3 : 4
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
If the magnetizing field on a ferromagnetic material is increased, its permeability ______.
decreases
increases
remains unchanged
first decreases and then increases
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
An iron cored coil is connected in series with an electric bulb with an AC source as shown in figure. When iron piece is taken out of the coil, the brightness of the bulb will ______.
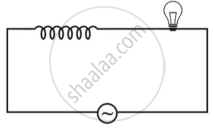
decrease
increase
remain unaffected
fluctuate
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Which of the following statement is NOT true about the properties of electromagnetic waves?
These waves do not require any material medium for their propagation
Both electric and magnetic field vectors attain the maxima and minima at the same time
The energy in electromagnetic wave is divided equally between electric and magnetic fields
Both electric and magnetic field vectors are parallel to each other
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
any of the four loops
the circular and elliptical loops
the rectangular, circular and elliptical loops
only the elliptical loops
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
In a Young’s double slit experiment, the path difference at a certain point on the screen between two interfering waves is `1/8`th of the wavelength. The ratio of intensity at this point to that at the centre of a bright fringe is close to ______.
0.80
0.74
0.94
0.85
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The work function for a metal surface is 4.14 eV. The threshold wavelength for this metal surface is ______.
4125 Å
2062.5 Å
3000 Å
6000 Å
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The radius of the innermost electron orbit of a hydrogen atom is 5.3 × 10–11m. The radius of the n = 3 orbit is ______.
1.01 × 10–11m
1.59 × 10–10m
2.12 × 10–10m
4.77 × 10–10m
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Which of the following statements about nuclear forces is not true?
The nuclear force between two nucleons falls rapidly to zero as their distance is more than a few femtometres.
The nuclear force is much weaker than the Coulomb force.
The force is attractive for distances larger than 0.8 fm and repulsive if they are separated by distances less than 0.8 fm.
The nuclear force between neutron-neutron, proton-neutron and proton-proton is approximately the same.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
If the reading of the voltmeter V1 is 40 V, then the reading of voltmeter V2 is ______.
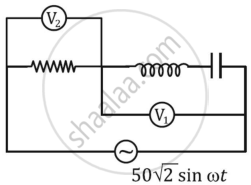
30 V
58 V
29 V
15 V
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
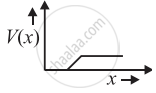
The electric potential V as a function of distance X is shown in the figure.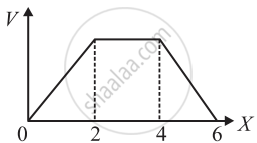
The graph of the magnitude of electric field intensity E as a function of X is ______.
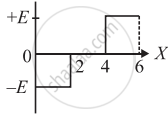
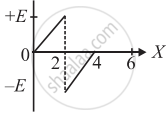
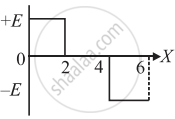
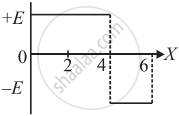
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
ASSERTION (A): The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases on doping.
REASON (R): Doping always increases the number of electrons in the semiconductor.
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
A is true but R is false
A is false and R is also false
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
ASSERTION (A): In an interference pattern observed in Young's double slit experiment, if the separation (d) between coherent sources as well as the distance (D) of the screen from the coherent sources both are reduced to 1/3rd, then new fringe width remains the same.
REASON (R): Fringe width is proportional to (d/D).
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
A is true but R is false
A is false and R is also false
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Assertion(A): The photoelectrons produced by a monochromatic light beam incident on a metal surface have a spread in their kinetic energies.
Reason(R): The energy of electrons emitted from inside the metal surface, is lost in collision with the other atoms in the metal.
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
A is true but R is false
A is false and R is also false
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifiers.
- λ3 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
Identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong. Also arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in figure when two specimens A and B are placed in it.
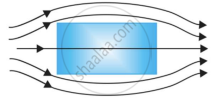 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
- Identify the specimen A and B.
- How is the magnetic susceptibility of specimen A different from that of specimen B?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Advertisements
What is the nuclear radius of 125Fe, if that of 27Al is 3.6 fermi?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
The short wavelength limit for the Lyman series of the hydrogen spectrum is 913.4 Å. Calculate the short wavelength limit for the Balmer series of the hydrogen spectrum.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A biconvex lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1.25 is immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Will the lens behave as a converging or a diverging lens? Give reason.
Chapter:
The figure shows a piece of pure semiconductor S in series with a variable resistor R and a source of constant voltage V. Should the value of R be increased or decreased to keep the reading of the ammeter constant, when semiconductor S is heated? Justify your answer
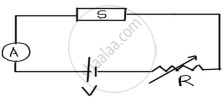
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
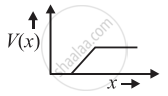 |
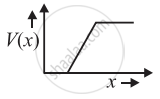 |
 |
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A narrow slit is illuminated by a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ equal to 6000 Å and the angular width of the central maximum in the resulting diffraction pattern is measured. When the slit is next illuminated by light of wavelength λ’, the angular width decreases by 30%. Calculate the value of the wavelength λ’.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude 17.7 × 10–22 C/m2. What is electric field intensity E:
- in the outer region of the first plate, and
- between the plates?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field produced by one exerts an attractive force on the other. Obtain the expression for this force and hence define 1 ampere.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
The magnetic field through a circular loop of wire 12 cm in radius and 8.5 Ω resistance, changes with time as shown in the figure. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Calculate the induced current in the loop and plot it as a function of time.
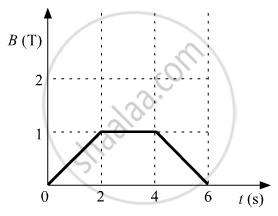
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
An a.c. source generating a voltage ε = ε0 sin ωt is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the expression for the current I flowing through it. Plot a graph of ε and I versus ωt to show that the current is ahead of the voltage by π/2.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
An ac voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied across a pure inductor of inductance L. Find an expression for the current i, flowing in the circuit and show mathematically that the current flowing through it lags behind the applied voltage by a phase angle of `π/2`. Also draw graphs of V and i versus ωt for the circuit.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Radiation of frequency 1015 Hz is incident on three photosensitive surfaces A, B and C. Following observations are recorded:
Surface A: no photoemission occurs
Surface B: photoemission occurs but the photoelectrons have zero kinetic energy.
Surface C: photo emission occurs and photoelectrons have some kinetic energy.
Using Einstein’s photo-electric equation, explain the three observations.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal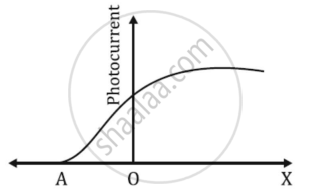
- What does X and A on the horizontal axis represent?
- Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation ʋ1, ʋ2 and ʋ3 (ʋ3 > ʋ2 > ʋ1) for the same intensity.
- Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I3 > I2 > I1) having the same frequency.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The ground state energy of hydrogen atoms is -13.6 eV. The photon emitted during the transition of electron from n = 3 to n = 1 unknown work function. The photoelectrons are emitted from the material with a maximum kinetic energy of 9 eV. Calculate the threshold wavelength of the material used.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Advertisements
Draw equipotential surfaces for (i) an electric dipole and (ii) two identical positive charges placed near each other.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6 × 10−3m2 and the separation between the plates is 3 mm.
- Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor.
- If this capacitor is connected to 100 V supply, what would be the charge on each plate?
- How would charge on the plates be affected, if a 3 mm thick mica sheet of k = 6 is inserted between the plates while the voltage supply remains connected?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Three charges –q, Q and –q are placed at equal distances on a straight line. If the potential energy of the system of these charges is zero, then what is the ratio Q:q?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Obtain the expression for the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell of radius R at a point distant r from the centre of the shell outside it.
- Draw a graph showing the variation of electric field intensity E with r, for r > R and r < R.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Explain the term ‘drift velocity’ of electrons in conductor. Hence obtain the expression for the current through a conductor in terms of ‘drift velocity’.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two cells of emfs E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 respectively are connected in parallel as shown in the figure. Deduce the expression for the
- equivalent emf of the combination
- equivalent internal resistance of the combination
- potential difference between the points A and B.
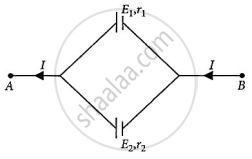
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in the analysis of electric circuits and explain them.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Derive the equation of the balanced state in a Wheatstone bridge using Kirchhoff’s laws.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Draw the graph showing intensity distribution of fringes with phase angle due to diffraction through a single slit. What is the width of the central maximum in comparison to that of a secondary maximum?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A ray PQ is incident normally on the face AB of a triangular prism of refracting angle 60° as shown in figure. The prism is made of a transparent material of refractive index `2/sqrt(3)`. Trace the path of the ray as it passes through the prism. Calculate the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation.
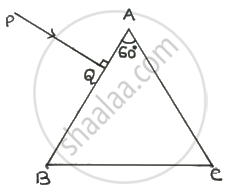
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write two points of difference between an interference pattern and a diffraction pattern.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
(i) A ray of light incident on face AB of an equilateral glass prism, shows minimum deviation of 30°. Calculate the speed of light through the prism.
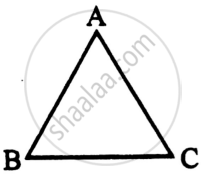
(ii) Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| A number of optical devices and instruments have been designed and developed such as periscope, binoculars, microscopes and telescopes utilising the reflecting and refracting properties of mirrors, lenses and prisms. Most of them are in common use. Our knowledge about the formation of images by the mirrors and lenses is the basic requirement for understanding the working of these devices. |
- Why the image formed at infinity is often considered most suitable for viewing. Explain
- In modern microscopes, multicomponent lenses are used for both the objective and the eyepiece. Why?
- Write two points of difference between a compound microscope and an astronomical telescope
OR
Write two distinct advantages of a reflecting type telescope over a refracting type telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
LED is a heavily doped P-N junction which under forward bias emits spontaneous radiation. When it is forward-biased, due to recombination of holes and electrons at the junction, energy is released in the form of photons. In the case of Si and Ge diode, the energy released in recombination lies in the infrared region. LEDs that can emit red, yellow, orange, green and blue light are commercially available. The semiconductor used for fabrication of visible LEDs must at least have a band gap of 1.8 eV. The compound semiconductor Gallium Arsenide – Phosphide is used for making LEDs of different colours.
|
- Why are LEDs made of compound semiconductor and not of elemental semiconductors?
- What should be the order of bandgap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
- A student connects the blue coloured LED as shown in the figure. The LED did not glow when switch S is closed. Explain why?
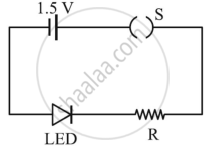
OR
iii. Draw V-I characteristic of a p-n junction diode in
(i) forward bias and (ii) reverse bias
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.

