Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The electric potential on the axis of an electric dipole at a distance ‘r from it’s centre is V. Then the potential at a point at the same distance on its equatorial line will be ______.
विकल्प
2V
-V
V/2
Zero
उत्तर
The electric potential on the axis of an electric dipole at a distance ‘r from it’s centre is V. Then the potential at a point at the same distance on its equatorial line will be zero.
Explanation:
Potential on the equatorial line of dipole is always zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A point charge +Q is placed at point O, as shown in the figure. Is the potential difference VA – VB positive, negative or zero?

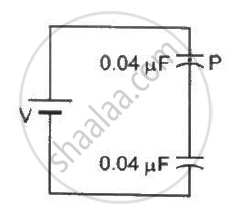
The particle P shown in figure has a mass of 10 mg and a charge of −0⋅01 µC. Each plate has a surface area 100 cm2 on one side. What potential difference V should be applied to the combination to hold the particle P in equilibrium?
Electric potential energy of two point charges q and q0 is ________.
If a positive charge moves opposite to the direction of the electric field, the field does _______ work on charge and potential energy ________.
A cube of metal is given a positive charge Q. For this system, which of the following statements is true?
From a point charge, there is a fixed point A. At A, there is an electric field of 500 V/m and potential difference of 3000 V. Distance between point charge and A will be ______.
A positively charged particle is released from rest in a uniform electric field. The electric potential energy of the charge ______.
A test charge is moved from lower potential point to a higher potential point. The potential energy of test charge will ______.
If a conductor has a potential V ≠ 0 and there are no charges anywhere else outside, then ______.
- there must be charges on the surface or inside itself.
- there cannot be any charge in the body of the conductor.
- there must be charges only on the surface.
- there must be charges inside the surface.
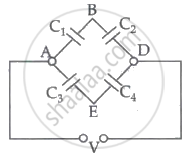
The potential difference between points B and E of the circuits is ______.