Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The electric potential on the axis of an electric dipole at a distance ‘r from it’s centre is V. Then the potential at a point at the same distance on its equatorial line will be ______.
पर्याय
2V
-V
V/2
Zero
उत्तर
The electric potential on the axis of an electric dipole at a distance ‘r from it’s centre is V. Then the potential at a point at the same distance on its equatorial line will be zero.
Explanation:
Potential on the equatorial line of dipole is always zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
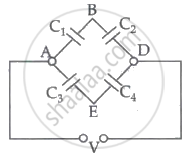
Take the potential of the point B in figure to be zero. (a) Find the potentials at the points C and D. (b) If a capacitor is connected between C and D, what charge will appear on this capacitor?
Show that electric potential at a point P, at a distance 'r' from a fixed point charge Q, is given by:
`v=(1/(4pi∈_0))Q/r`.
Answer the following question.
The magnitude of the electric field (in NC – 1) in a region varies with the distance r(in m) as
E = 10r + 5
By how much does the electric potential increase in moving from point at r = 11 m to a point at r = 10 m.
Electric potential energy of two point charges q and q0 is ________.
If a positive charge moves opposite to the direction of the electric field, the field does _______ work on charge and potential energy ________.
A positively charged particle is released from rest in a uniform electric field. The electric potential energy of the charge ______.
-
The metal plate divides the capacitor into two capacitors connected in parallel to each other.
-
The metal plate divides the capacitors into two capacitors connected in series with each other.
-
The metal plate is equivalent to a dielectric of zero dielectric constant.
If a conductor has a potential V ≠ 0 and there are no charges anywhere else outside, then ______.
The force acting on a particle in one dimension is F = ax - 2xβ3. The corresponding potential energy V(x), assuming V(0) = 0 is given by ______.
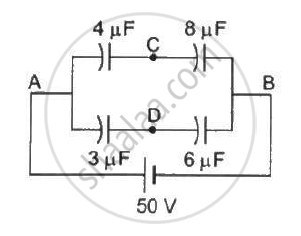
The potential difference between points B and E of the circuits is ______.