Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The temperature (T) dependence of resistivity of materials A and material B is represented by fig (i) and fig (ii) respectively. Identify material A and material B.
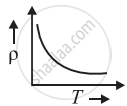 fig. (i) |
 fig. (ii) |
पर्याय
material A is copper and material B is germanium
material A is germanium and material B is copper
material A is nichrome and material B is germanium
material A is copper and material B is nichrome
उत्तर
material A is germanium and material B is copper
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A heating element using nichrome connected to a 230 V supply draws an initial current of 3.2 A which settles after a few seconds to a steady value of 2.8 A. What is the steady temperature of the heating element if the room temperature is 27.0°C? The temperature coefficient of resistance of nichrome averaged over the temperature range involved is 1.70 × 10−4 °C−1.
The order of coloured rings in a carbon resistor is red, yellow, blue and silver. The resistance of the
carbon resistor is:
a) 24 x 106 Ω ± 5%
b) 24 x 106 Ω ± 10%
c) 34 x 104 Ω ± 10%
d) 26 x 104 Ω ± 5%
Draw labelled graphs to show how electrical resistance varies with temperature for:
1) a metallic wire.
2) a piece of carbon
Show variation of resistivity of Si with temperature in a graph ?
Is work done by a battery always equal to the thermal energy developed in electrical circuit? What happens if a capacitor is connected in the circuit?
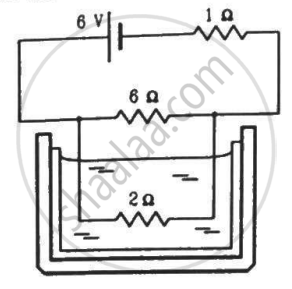
The 2.0 Ω resistor shown in the figure is dipped into a calorimeter containing water. The heat capacity of the calorimeter together with water is 2000 J K−1. (a) If the circuit is active for 15 minutes, what would be the rise in the temperature of the water? (b) Suppose the 6.0 Ω resistor gets burnt. What would be the rise in the temperature of the water in the next 15 minutes?
Define temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of a conductor.
A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 Ω at 0°C and 4.8 Ω at 150°C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material.
The specific resistance of all the metals is the most affected by ______
