Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
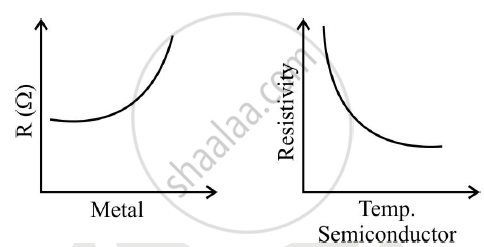
Draw labelled graphs to show how electrical resistance varies with temperature for:
1) a metallic wire.
2) a piece of carbon
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A silver wire has a resistance of 2.1 Ω at 27.5°C, and a resistance of 2.7 Ω at 100°C. Determine the temperature coefficient of resistivity of silver.
A heating element using nichrome connected to a 230 V supply draws an initial current of 3.2 A which settles after a few seconds to a steady value of 2.8 A. What is the steady temperature of the heating element if the room temperature is 27.0°C? The temperature coefficient of resistance of nichrome averaged over the temperature range involved is 1.70 × 10−4 °C−1.
The thermal energy developed in a current-carrying resistor is given by U = i2 Rt and also by U = Vit. Should we say that U is proportional to i2 or i?
Sometimes it is said that "heat is developed" in a resistance when there is an electric current in it. Recall that heat is defined as the energy being transferred due to temperature difference. Is the statement in quotes technically correct?
As temperature increases, the viscosity of liquids decreases considerably. Will this decrease the resistance of an electrolyte as the temperature increases?
A carbon resistor has coloured bands as shown in Figure 2 below. The resistance of the resistor is:
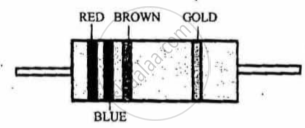
figure 2
A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 Ω at 0°C and 4.8 Ω at 150°C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material.
The temperature (T) dependence of resistivity of materials A and material B is represented by fig (i) and fig (ii) respectively. Identify material A and material B.
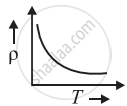 fig. (i) |
 fig. (ii) |
