Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A carbon resistor has coloured bands as shown in Figure 2 below. The resistance of the resistor is:
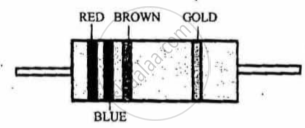
figure 2
पर्याय
260 ± 10%
260 ± 5%
2600 ± 5%
2600 ± 10%
उत्तर
A carbon resistor has coloured bands as shown in Figure 2 below. The resistance of the resistor is: 2600 ± 5%
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A silver wire has a resistance of 2.1 Ω at 27.5°C, and a resistance of 2.7 Ω at 100°C. Determine the temperature coefficient of resistivity of silver.
Show variation of resistivity of Si with temperature in a graph ?
Is work done by a battery always equal to the thermal energy developed in electrical circuit? What happens if a capacitor is connected in the circuit?
An electric kettle used to prepare tea, takes 2 minutes to boil 4 cups of water (1 cup contains 200 cc of water) if the room temperature is 25°C. (a) If the cost of power consumption is Re 1.00 per unit (1 unit = 1000 watt-hour), calculate the cost of boiling 4 cups of water. (b) What will be the corresponding cost if the room temperature drops to 5°C?
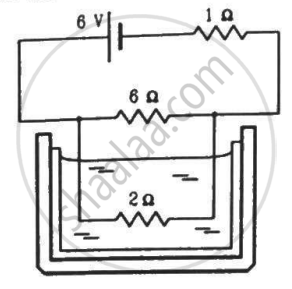
The 2.0 Ω resistor shown in the figure is dipped into a calorimeter containing water. The heat capacity of the calorimeter together with water is 2000 J K−1. (a) If the circuit is active for 15 minutes, what would be the rise in the temperature of the water? (b) Suppose the 6.0 Ω resistor gets burnt. What would be the rise in the temperature of the water in the next 15 minutes?
Define temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of a conductor.
An electrical cable of copper has just one wire of radius 9 mm. Its resistance is 5 ohm. This single copper wire of the cable is replaced by 6 different well insulated copper wires each of radius 3 mm. The total resistance of the cable will now be equal to ______.
By increasing the temperature, the specific resistance of a conductor and a semiconductor -
The specific resistance of all the metals is the most affected by ______
Temperature dependence of resistivity ρ(T) of semiconductors, insulators and metals is significantly based on the following factors:
- number of charge carriers can change with temperature T.
- time interval between two successive collisions can depend on T.
- length of material can be a function of T.
- mass of carriers is a function of T.
