Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of a conductor.
उत्तर
Temperature coefficient of resistance is defined as the change in resistance per unit original resistance at 0°C per degree centigrade rise of temperature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A silver wire has a resistance of 2.1 Ω at 27.5°C, and a resistance of 2.7 Ω at 100°C. Determine the temperature coefficient of resistivity of silver.
The order of coloured rings in a carbon resistor is red, yellow, blue and silver. The resistance of the
carbon resistor is:
a) 24 x 106 Ω ± 5%
b) 24 x 106 Ω ± 10%
c) 34 x 104 Ω ± 10%
d) 26 x 104 Ω ± 5%
Consider a circuit containing an ideal battery connected to a resistor. Do "work done by the battery" and "the thermal energy developed" represent two names of the same physical quantity?
Is work done by a battery always equal to the thermal energy developed in electrical circuit? What happens if a capacitor is connected in the circuit?
Consider the following statements regarding a thermocouple.
(A) The neutral temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
(B) The inversion temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
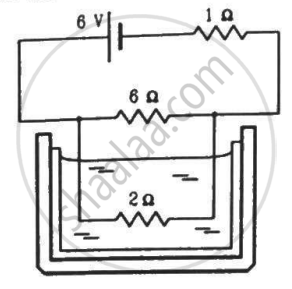
The 2.0 Ω resistor shown in the figure is dipped into a calorimeter containing water. The heat capacity of the calorimeter together with water is 2000 J K−1. (a) If the circuit is active for 15 minutes, what would be the rise in the temperature of the water? (b) Suppose the 6.0 Ω resistor gets burnt. What would be the rise in the temperature of the water in the next 15 minutes?
A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 Ω at 0°C and 4.8 Ω at 150°C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material.
The specific resistance of all the metals is the most affected by ______
