Advertisements
Chapters
1: Factors of Production
Theory of Demand and Supply
2: Elementary Theory of Demand
3: Elasticity of Demand
▶ 4: Theory of Supply
Market
5: Meaning and Types of Markets
Banking in India
6: Meaning and Functions of Money
7: Commercial Banks
8: Central Bank
9: Introduction to Public Finance
10: Public Revenue
11: Public Expenditure
12: Public Debt
Inflation
13: Inflation
Consumer Awareness
14: Consumer Awareness
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Theory of Supply Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Theory of Supply - Shaalaa.com](/images/economics-english-class-10-icse_6:ca738c8e53b2465d96b5253bb7b17d70.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Theory of Supply
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CISCE Goyal Brothers Prakashan for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE 4 Theory of Supply Exercise [Pages 95 - 100]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Following is an essential feature of supply:
Total quantity of a product available for sale at a particular point of time.
Quantity of a product offered for sale at a certain price.
Supply is a stock variable.
All the above
Which one of the following is not a feature of supply?
Price of the commodity
Period of time
Willingness to buy
Quantity of the commodity
Other things remaining unchanged, change in supply due to increase in price is called ______.
Contraction of supply
Expansion of supply
Decrease in supply
Increase in supply
The diagram shows the supply of cotton clothes which of the following would be the case of movement from A to B?
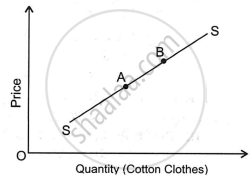
An increase in price of cotton clothes
An increase in price of silk clothes
An improvement in technology
An increase in the number of producers
Law of supply states that ______.
There is direct relation between price and supply.
There is inverse relation between price and supply.
There is direct and proportionate relation between price and supply.
None of these
Law of supply does not apply to ______.
Agricultural goods
Perishable goods
Both (a) and (b)
Neither (a) nor (b)
The law of supply is based on the assumption of ______.
Constant technology
The commodity is divisible
The prices of factors of production remain constant
All the above
Due to installation of a machine with latest technology, the cost of production has decreased. It will lead to ______.
Expansion in supply
Increase in supply
Contraction in supply
Decrease in supply
In the case of ______, supply falls at the same price.
Decrease in supply
Contraction in supply
Increase in supply
Expansion in supply
The following supply curve shifts from SS to S1S1. It may be due to ______.
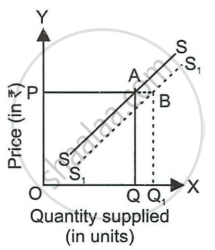
Decrease in Taxes
Upgradation of technology
Fall in the price of inputs
All of the above
Which of the following does not cause shift of supply curve of a good?
Price of input
Price of the good
Goods and Services Tax
Subsidy
Which of the following factor may cause decrease in supply?
Fall in price of given product
Fall in price of factors of production
Decrease in number of firms
Expected fall in the price of given product in future
Increase or decrease in supply means ______.
shift of supply curve
movement along the supply curve
elastic supply
None of these
Identify the incorrect statement from the following:
Supply is always stated with reference to some price.
The amount supplied of a commodity will be different at different prices.
Supply is related to point of time.
Supply is different from stock.
What is the degree of elasticity of supply in the diagram?
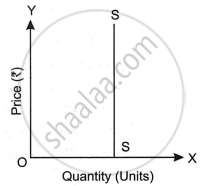
Infinity
One
Zero
None of these
A 10 per cent increase in price of a good causes 5 per cent increase in its quantity supplied, elasticity of supply will be ______.
Inelastic
Elastic
Perfectly elastic
Perfectly inelastic
When price of a·product rises by 10% its quantity supplied also rises by 10%. Find out price elasticity.
Zero
Infinity
1
10
Which of the following does not cause shift of supply curve of a good?
Price of input
Price of the good
Goods and Services Tax
Subsidy
Which of the following measures of price elasticity shows elasticity shows elastic supply?
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
In case of ______, supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to the Y-axis.
Perfectly Elastic Supply
Unitary Elastic Supply
Perfectly Inelastic Supply
Less Elastic Supply
Which of the following measures of price elasticity shows inelastic supply?
0
0.5
1
1.5
Price elasticity of supply is likely to be ______ in the long run.
perfectly inelastic
perfectly elastic
elastic
inelastic
The supply of perishable goods like milk, vegetables, fish is ______.
Inelastic
Elastic
Perfectly elastic
None of these
When there is no change in price, but quality supplied changes, it implies a situation of ______.
Relatively elastic supply
Relatively in elastic supply
Perfectly inelastic supply
Perfectly elastic supply
If the price of factors of production increases, then the supply will ______.
Decrease
Increase
Zero
None of these
Cotton and cotton seeds are examples of ______ supply.
jointly produced goods
inferior goods
composite goods
inferior goods
If the cost of production is less than the supply will ______.
decrease
increase
be constant
be negative
The producers prefer to supply more when prices are ______.
Low
High
Negative
Positive
When the government gives tax ______ than the supply of goods will increase.
Imposition
Restriction
Concession
Perfection
When producers expect price rise in the future, they would like to ______ the present supply of their commodities.
Increase
Reduce
Keep Constant
Stop
Price of the commodity and quantity supplied of that commodity is ______ related.
Inversely
Cross
Negative
Directly
If the number of firms producing a particular commodity increases, the market supply of that commodity will be ______.
Increase
Decrease
Remain constant
Become negative
Increase in the tax on a commodity will lead to ______ in the supply of the commodity.
Fixing
No change
Increase
Decrease
______ represents downward movement along the same supply curve.
Increase in supply
Decrease in supply
Contraction of supply
Extension of supply
Short Answer Type Questions
Define the term supply.
Define the term supply.
How is supply different from stock?
Explain the determinants of supply?
Draw a supply curve.
Explain how the supply of a commodity is affected by the prices of other related commodities. Give suitable examples.
Explain the law of supply.
Price and Supply move in the same direction. Justify the statement.
Mention two assumptions of the law of supply.
Construct an imaginary individual supply schedule. Draw an individual supply curve based on an imaginary individual supply schedule.
Derive market supply schedule and curve from the following hypothetical individual supply schedules of two firms A and B.
| Price | SA | SB |
| 2 | 10 | 7 |
| 3 | 12 | 8 |
| 4 | 14 | 9 |
Distinguish between a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply.
What is an extension of supply?
What is contraction of supply?
What do you understand by shifts of the supply curve?
Point out two factors that lead to increase in supply.
Mention two factors which cause decrease in supply.
How does an improvement in production technology influence the supply curve of a firm?
If the government of India levies excise duty on sugar, in which direction will the supply of sugar shift?
Define elasticity of supply.
When is the supply of a commodity is called elastic?
Draw a straight line supply showing elasticity greater than one.
Draw a perfectly elastic supply curve.
Draw a perfectly inelastic supply curve.
Why does the quantity supplied increases with a rise in price? Give two reasons.
There are three identical firms in a market. The following table shows the supply schedule of firm 1. Compute the market supply schedule.
| Price (₹ per unit): | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Supply (units): | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
The following diagram shows the supply curve of three commodities. Rank their price elasticity.
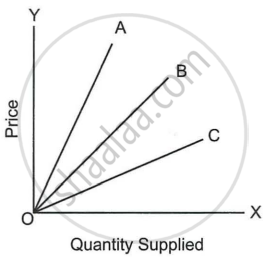
Study the graph and identify the supply curves S1 and S3 with respect to its time elements.
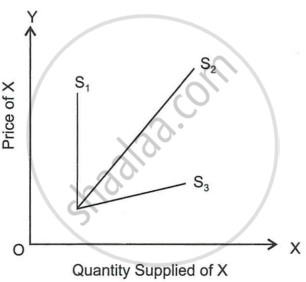
Draw a well-labelled diagram showing the price elasticity of supply of a commodity starting from the origin.
Explain briefly the impact of the cost of production on the elasticity of supply.
Long Answer Type Questions
Distinguish between supply and stock.
Explain four factors on which the supply of a commodity depends.
State and explain the law of supply with the help of a diagram.
Discuss any two exceptions to the law of supply.
How is a market supply schedule attained from individual supply schedules of a commodity?
Explain three factors causing a shift of the supply curve.
Distinguish between a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply.
Define the term supply.
Explain three reasons for the rightward shift of the supply curve.
What is meant by shift in supply?
Explain three determinants of a leftward shift of the supply curve.
Distinguish between expansion of supply and increase in supply.
Define a decrease in supply.
Explain three determinants of a leftward shift of the supply curve.
Distinguish between contraction and decrease in supply.
With the help of a diagram, explain the meaning of the increase in supply.
With the help of a diagram, explain the meaning of a decrease in supply.
Explain five determinants of shift in supply curve.
Define elasticity of supply.
Explain any four determinants of elasticity of supply.
What is meant by elasticity of supply?
Using graphs, explain any four types of elasticity of supply.
With the help of a suitable diagram, explain the following degree of elasticity of supply.
Es = ∞
With the help of a suitable diagram, explain the following degree of elasticity of supply.
Es > 1
Explain the law of supply.
Explain any three factors other than price which determine supply in the market.
Define a relatively elastic supply.
Draw relatively elastic supply.
Define a relatively inelastic supply.
Draw relatively inelastic supply.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE 4 Theory of Supply QUESTION BANK [Pages 100 - 104]
Define the term supply.
Distinguish between supply and stock.
What is a supply schedule?
What is market supply?
What is supply function?
State any two factors determining supply.
Define supply curve.
Explain the law of supply.
What is meant by movement along the supply curve (or change in quantity supplied)?
What is meant by shift in supply?
What is an extension of supply?
What is contraction of supply?
What causes a downward movement along a supply curve?
What causes an upward movement along the supply curve of a commodity?
What is meant by 'increase' in supply?
Define a decrease in supply.
How does technological progress affect the supply curve of a firm?
If a farmer grows rice and wheat, how will a decrease in the price of wheat affect the supply curve of rice?
How does the imposition of taxe affect the supply curve of a firm?
How does an decrease in price of an input affect the supply curve of a firm?
How does a increase in the number of firms in a market affect the market supply curve?
Define elasticity of supply.
If the price of a commodity falls by 10% and consequently, the quantity supplied decreases by 20%, what will be its elasticity of supply?
What is meant by inelastic supply?
What do you mean by elastic supply?
When is supply of a good unitary elastic?
What is meant by perfectly elastic supply?
What do you mean by perfectly inelastic supply?
Price elasticity of supply of a good is 0.8. Is the supply 'elastic' or 'inelastic', and why?
Why is the supply of eggs inelastic?
Study the graph and identify the supply curves S1 and S3 with respect to its time elements.

Define the term supply.
State and explain the law of supply with the help of a diagram.
Give two reasons for the positive slope of the supply curve.
With the help of a hypothetical supply schedule, draw a supply curve.
State one exception to the law of supply.
Explain the following diagram.
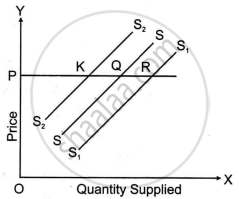
With the help of a diagram, define an increase in supply.
Discuss four factors which determine this phenomenon.
With the help of a diagram, define a decrease in supply.
Mention two factors which cause decrease in supply.
How does an improvement in production technology influence the supply curve of a firm?
What effect does increased input prices have on the supply curve of a commodity? Draw a diagram to explain your answer.
Explain the determinants of supply?
With the help of a suitable diagram, explain the following degree of elasticity of supply.
Es = ∞
With the help of a suitable diagram, explain the following degree of elasticity of supply.
Es > 1
Explain the percentage method of measuring price elasticity of supply.
Solutions for 4: Theory of Supply
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Theory of Supply Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Theory of Supply - Shaalaa.com](/images/economics-english-class-10-icse_6:ca738c8e53b2465d96b5253bb7b17d70.jpg)
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Theory of Supply
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Mathematics Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 4 (Theory of Supply) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Goyal Brothers Prakashan textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 Theory of Supply are Concept of Supply, Difference Between Supply and Stock, Types of Supply, Factors Affecting Supply (Or Determinants of Supply), Supply Schedule, Supply Curve, Law of Supply, Statement of the Law of Supply, Assumptions of the Law of Supply, Explanation of the Law of Supply, Reasons Behind the Operation of the Law of Supply, Exceptions to the Law of Supply, Change in Quantity Supplied (Or Movements Along the Supply Curve), Change in Supply (Or Shifts of Supply Curve), Distinction Between Change in Quantity Supplied (Or Movement Along Supply Curve and Change in Supply Or Shift of the Supply Curve), Distinction Between Expansion in Supply and Increase in Supply, Distinction Between Contraction in Supply and Decrease in Supply, Elasticity of Supply.
Using Goyal Brothers Prakashan Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Theory of Supply exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Goyal Brothers Prakashan Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Goyal Brothers Prakashan Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Theory of Supply Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
