Advertisements
Chapters
1: Factors of Production
Theory of Demand and Supply
2: Elementary Theory of Demand
3: Elasticity of Demand
4: Theory of Supply
Market
▶ 5: Meaning and Types of Markets
Banking in India
6: Meaning and Functions of Money
7: Commercial Banks
8: Central Bank
9: Introduction to Public Finance
10: Public Revenue
11: Public Expenditure
12: Public Debt
Inflation
13: Inflation
Consumer Awareness
14: Consumer Awareness
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Meaning and Types of Markets Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Meaning and Types of Markets - Shaalaa.com](/images/economics-english-class-10-icse_6:ca738c8e53b2465d96b5253bb7b17d70.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Meaning and Types of Markets
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CISCE Goyal Brothers Prakashan for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Meaning and Types of Markets Exercise [Pages 113 - 117]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Following is the feature of perfect competition:
Product differentiation
Homogeneous product
Barriers to entry
Less elastic
Following is not the feature of perfect competition:
Very large number of buyers and sellers
Homogeneous product
Free entry or exit of firms
Selling costs
'Homogeneous products' is a characteristic of ______.
Perfect competition only
Pure oligopoly only
Both Perfect competition only and Pure oligopoly only
None of the above
Differentiated products is a characteristic of ______.
Monopolistic competition only
Imperfect oligopoly only
Both monopolistic competition and imperfect oligopoly only
Monopoly
'A few big sellers' is a characteristic of ______.
Perfect competition
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
All the above
Marginal revenue of a firm is constant throughout under:
Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
All the above
A seller cannot influence the market price under:
Perfect competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
All the above
In monopolistic competition, there are ______.
Few firms selling differentiated products.
Large number of firms selling differentiated products.
Large number of firms selling homogeneous products.
Few firms selling a homogeneous products.
Identify the feature of monopoly market from the following:
A single seller
A single buyer
Homogeneous goods
Product differentiation
Indian Railways is an example of ______.
Monopolistic competition
Perfect competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Identify the market form for telecom industry in India.
Perfect competition
Monopolistic competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
______ is relevant to perfect competition.
Perfectly inelastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand
Downward sloping demand curve
Highly elastic demand curve
Which of the following is an example of oligopoly in India?
Car industry
Textile industry
Shampoos
Restaurant industry
There is inverse relation between price and demand for the product of a firm under ______.
Monopoly only
Monopolistic competition only
Both under monopoly and monopolistic competition
Perfect competition only
A market where homogeneous products are sold with no control over price by an individual firm or a buyer is ______.
Monopolistically competitive market
Perfectly competitive market
Monopoly
Monopsony
Oligopoly
The following diagram represents the demand curve of a firm under ______.
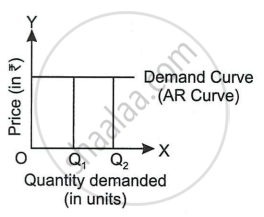
Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
In which market form, marginal revenue is equal to price?
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
The following diagram represents the demand curve of a firm under ______.
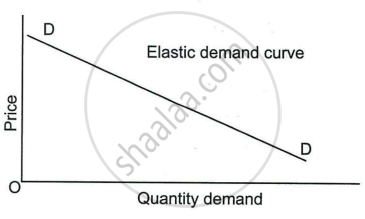
Perfect competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
There are a few large firms under ______.
Perfect competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
A ______ firm can sell the same product at different prices to different buyers.
Competitive
Oligopolistic
Monopoly
None of these
Under a monopoly market, a firm/seller has ______.
Partial control over price
Full control over price
No control over price
None of these
Homogeneous products are sold under ______.
Oligopoly market
Monopoly market
Perfect competition
Monopolistic competition
There are a large number of buyers and sellers under a ______ market.
Monopoly market
Perfect market
Oligopoly market
All of the above
Oligopoly is a market situation in which there are only a ______ sellers in the industry.
Few
Large
Futuristic
Maximum
______ is essential for a market to be called as perfect competition.
Large number of buyers and sellers
Restricted entry and exit
No substitutes
Differentiated goods
A differentiated product has ______.
Many perfect substitutes
No close substitutes
Close but not perfect substitute
No substitute of any kind
______ goods refer to those products which are identical in quality, shape, size, color, etc.
Heterogeneous
Homogeneous
Differentiated
Slightly differentiated
In which market form is the firm a price taker?
Money market
Monopoly
Perfect competition
Capital market
Which of the following describes a monopoly firm?
Single seller
No barrier to entry
Many substitutes
Many sellers
Which of the following market types has a large number of firms that sell similar but slightly different products?
Perfect competition
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Monopoly
Firms under ______ are free to enter or leave the industry any time.
Perfect competition
Pure oligopoly
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Short Answer Type Questions
Define the term market.
What is perfect competition?
What is meant by pure competition?
Mention two features of monopoly.
Producers in a monopoly are price makers. Briefly explain.
There are no substitute goods in a monopoly market. Give a reason to support your answer.
Mention one feature of a monopoly market.
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Define monopolistic competition.
What is meant by oligopoly?
Give an example of oligopoly.
Give two examples of monopolistically competitive market.
Give two reasons why monopolistic competition is the most realistic form of a market.
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Mention two features of monopoly.
Discuss any two features of a monopolistically competitive market.
What is meant by product differentiation?
To which market is product differentiation relevant?
What are selling costs?
Why is there no need for selling cost under perfect competition?
In which form of market is the seller a price taker? Justify your answer.
Identify the market form of the following:
The Government of India is the sole buyer of fighter aircrafts.
Identify the market form of the following:
Goods sold are homogeneous.
Identify the market form of the following:
Motor car market in India.
Identify the market form of the following:
Market for toilet soaps in India.
Identify the market form for the following:
Railways in India.
Identify the market form for the following:
Textile industry in India.
Identify the market form for the following:
Perfectly elastic demand.
Identify the market form for the following:
Telecom industry in India.
State the market form of the following commodity.
Railways
State the market form of the following commodity.
Automobiles
State the market form of the following commodity.
Shampoos
State the market form of the following commodity.
Fighter Aircrafts
Identify the market form for the item given below:
A single seller
Identify the market form for the item given below:
Homogeneous goods
Identify the market form for the item given below:
Product differentiation
Identify the market form for the item given below:
A single buyer
Why do producers incur high selling costs in an imperfect market?
State the similarities between monopolistic competition and monopoly.
In which form of market do producers and consumers have perfect knowledge about the market conditions?
State two dissimilarities between Monopolistic competition and Perfect competition.
Long Answer Type Questions
What is meant by 'market' in economics?
Discuss the characteristics of a market.
What is perfect competition?
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Define monopoly.
Mention two features of monopoly.
What is perfect competition?
Discuss three differences between a perfectly competitive market and a monopoly.
Define monopoly.
Discuss any four differences between monopoly and monopolistic competition.
Define monopolistic competition.
Discuss any two features of a monopolistically competitive market.
Define monopoly.
Discuss any four differences between monopoly and monopolistic competition.
Explain any four factors that lead to the emergence of monopoly.
Explain the following feature of perfect competition:
Large number of buyers and sellers
Explain the following feature of perfect competition:
Homogeneous products
Product differentiation is practised in monopolistic competition? Give reasons.
Monopolistic competition is the perfect blending of monopoly and perfect competition. Explain.
Explain any two similarities between a perfect market and a monopolistically competitive market.
State two dissimilarities between Monopolistic competition and Perfect competition.
With the help of an example explain the meaning of price discrimination.
To which market is price discrimination relevant?
Explain any two similarities between a perfect market and a monopolistically competitive market.
Define monopolistic competition.
Give two examples of monopolistically competitive market.
Discuss any two features of a monopolistically competitive market.
Explain any two similarities between a perfect market and a monopolistically competitive market.
State two dissimilarities between Monopolistic competition and Perfect competition.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Meaning and Types of Markets QUESTION BANK [Pages 117 - 121]
Define the term market.
What is perfect competition?
What is meant by pure competition?
Define monopoly.
Give an example of monopoly.
Define monopolistic competition.
Give two examples of monopolistically competitive market.
Name the characteristic which makes monopolistic competition different from perfect competition.
What do you mean by homogeneous products?
To which market form are homogeneous products relevant?
What is meant by product differentiation?
To which market is product differentiation relevant?
What is meant by the term 'price taker'?
Under which market form firm is price taker?
What is a price making firm?
Why an individual firm under perfect competition cannot influence the market price?
Which market form has the least number of producers?
What induces new firms to enter an industry?
What is meant by barriers to entry?
What is the effect on price when a perfectly competitive firm tries to sell more?
What is the effect on price when a monopoly firm tries to sell more?
What is meant by oligopoly?
Give an example of oligopoly.
What is the difference between perfect and imperfect oligopoly?
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Explain any two similarities between a perfect market and a monopolistically competitive market.
State the similarities between monopolistic competition and monopoly.
Producers in a monopoly are price makers. Briefly explain.
What do you mean by price discrimination?
To which market is price discrimination relevant?
In which market form are goods sold at a uniform price?
Why is there no need for selling cost under perfect competition?
Name the market which has characteristics both of monopoly and perfect competition.
Give two reasons why monopolistic competition is the most realistic form of a market.
What are selling costs?
Why are selling costs incurred?
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Mention two features of monopoly.
Discuss any two features of a monopolistically competitive market.
State the advantage of monopolistic competition over monopoly.
Why is the demand curve under monopoly less elastic as compared to the demand curve under monopolistic competition?
What does perfectly elastic demand curve faced by a competitive firm indicate?
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Mention two features of monopoly.
Discuss any two features of a monopolistically competitive market.
Explain any two similarities between a perfect market and a monopolistically competitive market.
State two dissimilarities between Monopolistic competition and Perfect competition.
Discuss three differences between a perfectly competitive market and a monopoly.
Discuss any four differences between monopoly and monopolistic competition.
State two dissimilarities between Monopolistic competition and Perfect competition.
What is meant by oligopoly?
In what respects does oligopoly differ from monopoly?
Identify the market form from the following.
Firm is a price maker.
Identify the market form for the item given below:
Product differentiation
Identify the market form from the following.
Price discrimination
Identify the market form from the following.
Perfect knowledge
Identify the market form from the following:
A few large sellers
Elaborate the price discrimination feature of monopoly.
Solutions for 5: Meaning and Types of Markets
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Meaning and Types of Markets Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Meaning and Types of Markets - Shaalaa.com](/images/economics-english-class-10-icse_6:ca738c8e53b2465d96b5253bb7b17d70.jpg)
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Meaning and Types of Markets
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Mathematics Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 5 (Meaning and Types of Markets) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Goyal Brothers Prakashan textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 Meaning and Types of Markets are Concept of Market, Forms of Market Structure, Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, Monopsony, Distinction Between Perfect Competition, Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition, Similarities Between Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Competition, Similarities Between Monopolistic Competition and Monopoly.
Using Goyal Brothers Prakashan Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Meaning and Types of Markets exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Goyal Brothers Prakashan Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Goyal Brothers Prakashan Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Meaning and Types of Markets Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Economics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
