Topics
Periodic Table, Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Periodic Properties
- Shells (Orbits)
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Chemical Reactivity
- Ionisation Potential (Ionisation Energy)
- Electron Affinity
- Electronegativity
- Atomic Number (Z), Mass Number (A), and Number of Neutrons (n)
- Atomic Mass
- Study of Specific Groups in Periodic Table
- Group I (Alkali Metals)
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Bonding
- Chemical Bond
- Types of Chemical Bond
- Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
- Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
- The Covalent Bond
- Types of Covalent Bond
- Formation of Covalent Bond
- Properties and Comparison of Electrovalent and Covalent Compounds
- Effect of Electricity on Electrovalent and Covalent Compounds
- Coordinate Bond
- Formation of Coordinate Bond
Study of Acids, Bases and Salts
- Acids
- Classification of Acids
- Preparation of Acids
- Properties of Acids
- Uses of Acids
- Bases (Alkalis)
- Classification of Bases (Alkalis)
- Preparation of Bases
- Properties of Bases (Alkalis)
- Uses of Bases
- Making of natural indicator
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Salts
- Classification of Salts
- Methods of Preparation of Soluble Salts
- Preparation of Insoluble Salts
- Laboratory Preparation of Some Salts
- Laboratory Preparation of Iron (III) Chloride
- Laboratory Preparation of Zinc Sulphate Crystals from Zinc and Sulphuric Acid
- Laboratory Preparation of Lead Chloride and Calcium Carbonate
- Laboratory Preparation of an Acid Salt Sodium Bicarbonate
- Neutralisation
- Laboratory Preparation of Copper (II) Sulphate (Or Blue Vitriol)
- Laboratory Preparation of Sodium Sulphate Crystals
- Properties of Salts
Analytical Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Colours of the Salts and Their Solutions
- Action of Sodium Hydroxide Solution on Certain Metallic Salt Solutions
- Action of Ammonium Hydroxide on Certain Salt Solutions
- Action of Alkalis on Certain Metals
- Action of Alkalis on Metal Oxides
Mole Concept and Stoichiometry
- The Gas Laws
- Fundamental Laws of Gases
- Pressure and Volume Relationship or Bolye's Law
- Temperature - Volume Relationship or Charles's Law
- Gay Lussac’s Law of Combining Volumes
- Avogadro’s Law
- Gas Equation
- Standard Temperature Pressure (S.T.P.)
- Absolute Zero
- Atomic Mass
- Molecular Mass
- Mole Concept
- Relationship Between Vapour Density and Relative Molecular Mass
- Percentage Composition, Empirical and Molecular Formula
- Empirical Formula of a Compound
- Determination of Empirical Formula
- Determination of Molecular Formula
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Numerical Problems of Chemical Equation
Electrolysis
- Electrolysis
- Electrolytes
- Nonelectrolyte
- Electrochemical Cells
- Electrodes
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Arrhenius Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation
- Electrochemical Series
- Preferential Or Selective Discharge of Ions at Electrodes
- Examples of Electrolysis
- Electrolysis of Molten Lead Bromid
- Electrolysis of Acidified Water Using Platinum Electrodes
- Electrolysis of Copper Sulphate Solution Using Platinum Anode and Copper Or Platinum Cathode
- Electrolysis of Aqueous Copper Sulphate - Using Copper Electrodes
- Applications of Electrolysis
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Mineral Resources
- Ores
- Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Types of Separation or Concentration of an Ore
- Conversion of Concentrated Ore to Its Oxide
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Reduction of Metal Oxides to Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Metallurgy of Aluminium
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Refining of Aluminium
- Alloy
- Making Alloys
- Some Common Alloys
- Prevention of Corrosion
Study of Compounds
Hydrogen Chloride
- Hydrogen Chloride
- General Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas
- Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas
- Physical Properties of Hydrogen Chloride Gas
- Chemical Properties of Hydrogen Chloride Gas
- Hydrochloric Acid
- Laboratory Method of Preparation of Hydrochloric Acid
- Properties of Hydrochloric Acid
- Uses of Hydrochloric Acid
- Tests for Hydrogen Chloride and Hydrochloric Acid
Ammonia
- Ammonia
- General Methods of Preparation of Ammonia Gas
- Laboratory Preparation of Ammonia Gas
- Preparation of Aqueous Ammonia
- Manufacture of Ammonia (Haber's Process)
- Physical Properties of Ammonia
- Chemical Properties of Ammonia
- Tests for Ammonia Gas and Ammonium Ion
- Uses of Ammonia
Nitric Acid
- Nitric Acid
- Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid
- Manufacture of Nitric Acid
- Physical Properties of Nitric Acid
- Chemical Properties of Nitric Acid
- Uses of Nitric Acid
- Tests for Nitric Acid and Nitrates
- Effects of Heat on Nitrates
Sulphuric Acid
- Sulphuric Acid
- Preparation of Sulphuric Acid
- Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid (Constant Process)
- Physical Properties of Sulphuric Acid
- Chemical Properties of Sulphuric Acid
- Uses of Sulphuric Acid
- Tests for Sulphuric Acid and Sulphates
Organic Chemistry
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Classification of Compounds of Carbon
- Organic Compounds
- Special Features of Carbon
- Organic Compounds in Daily Life
- Hydrocarbons
- Classification of Organic Compounds Based on the Pattern of Carbon Chain
- Classification of Organic Compound Based on the Kind of Atoms
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons
- IUPAC Nomenclature of other classes
- Alkyl Group
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Isomers
- Hydrocarbons: Alkanes
- Methane
- Laboratory Preparation of Methane
- Ethane
- Laboratory Preparation of Ethane
- Hydrocarbons: Alkenes
- Ethene (Ethylene)
- Preparation of Ethene (Ethylene)
- Hydrocarbons: Alkynes
- Ethyne
- Laboratory Preparation of Ethyne
- Alcohol
- Ethanol
- Laboratory Preparation of Ethanol
- Carboxylic Acids
- Ethanoic Acid
Practical Work
- Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen
- Laboratory Preparation of Oxygen
- Laboratory Preparation of Carbon Dioxide
- Laboratory Preparation of Chlorine
- Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas
- Laboratory Preparation of Sulphur Dioxide
- Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen Sulphide
- Laboratory Preparation of Ammonia Gas
- Laboratory Preparation of Water Vapour
- Laboratory Preparation of Nitrogen Dioxide
- Action of Heat on a Given Substance
- Action of Dilute Sulphuric Acid on a Given Substance
- Dry Test
- Recognition of Substances by Colour
- Recognition of Substances by Odour
- Recognition of Substances by Physical State
- Recognition of Substances by Action of Heat
- Flame Test
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Indicators
- Identification of Ions
- Identification of Cations
- Identification of Anions
- Distinction Between Colourless Solutions of Dilute Acids and Alkalis
- Distinguish Between Black Copper Oxide and Black Manganese Dioxide
- Introduction
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonds
- Lewis Dot Structure
Introduction:
A bond is a force that holds two or more atoms together in a molecule or compound. Bonds are formed by the interaction of valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The force of attraction between atoms, known as a chemical bond, enables the formation of chemical compounds. Atoms form chemical bonds to attain a stable electron configuration (like noble gases with a complete octet or duplet).
Types of chemical bonds include:
- Ionic bond (transfer of electrons)
- Covalent bond (sharing of electrons)
- Metallic bond (pooling of electrons among metals)
Kossel–Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonds:
Walther Kossel and Gilbert N. Lewis independently proposed that atoms form bonds to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
- Their model is based on the octet rule: Atoms tend to have 8 electrons in their outermost shell (or 2 for small atoms like hydrogen and helium).
- Valence electrons are used in bonding. Atoms interact through their outermost electrons.
Ionic Bond Formation (Kossel): Atoms of metals lose electrons, becoming positively charged ions (cations). Nonmetals gain electrons, becoming negatively charged ions (anions). The opposite charges attract, forming an ionic bond (e.g., NaCl).
Covalent Bond Formation (Lewis): Nonmetals share valence electrons with each other to complete their octets. This forms a covalent bond (e.g., H₂O, CO₂).
Lewis Dot Structure:
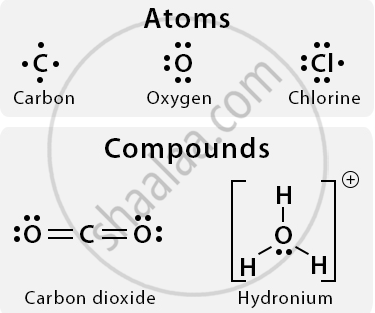
The Lewis dot structure is a diagram that represents the valence electrons of an atom using dots placed around the chemical symbol. It helps visualise how atoms form bonds by sharing or transferring electrons.
Steps to Draw a Lewis Dot Structure:
- Write the Element Symbol: Use the chemical symbol of the element (e.g., H for hydrogen, O for oxygen).
- Determine Valence Electrons: Identify the number of valence electrons (outermost shell electrons) for the atom.
- Place Dots Around the Symbol: Place dots to represent each valence electron around the element symbol. Use up to 2 dots per side (top, bottom, left, right) until all electrons are shown.
- For molecules: Show shared electrons (bonding pairs) between atoms with dots or lines.
For example,
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [138]
Complete the following table:
| a. | Dativebond | ______ |
| b. | CaH2 → Ca+H2 | ______ |
| c. | ______ | Reduction |
| d. | ______ | Redox reaction |
Five atoms are labelled from A to E.
| Atoms | Mass No. | Atomic No. |
| A | 40 | 20 |
| B | 19 | 9 |
| C | 7 | 3 |
| D | 16 | 8 |
| E | 14 | 7 |
(a) Which one of these atoms:
(i) contains 7 protons,
(ii) has an electronic configuration 2, 7?
(b) Write down the formula of the compound formed between C and D.
(c) predict which are: (i) metals, (ii) non-metals?
