| Symbol: Al |
| Color: Silver white |
| Atomic Number: 13 |
| Electronic Configuration: 2, 8, 3 |
| Valency: 3 |
1. Concentration of Bauxite Ore
Bauxite contains impurities like silica (SiO₂), ferric oxide (Fe₂O₃), and titanium oxide (TiO₂), which are removed using Bayer’s process or Hall’s process.A. Bayer’s Process (Using NaOH)
Bauxite is ground and heated with concentrated NaOH at 140–150°C under high pressure. Aluminium oxide reacts with NaOH, forming sodium aluminate (soluble).
- Al₂O₃⋅2H₂O + 2NaOH→2NaAlO₂ + 3H₂O
Iron oxide remains undissolved and is filtered out. Silica dissolves, forming sodium silicate. Sodium aluminate solution is cooled and diluted, causing Al(OH)₃ precipitation.
- NaAlO₂ + 2H₂O → NaOH + Al(OH)₃↓
Al(OH)₃ is heated at 1000°C, producing pure alumina (Al₂O₃).
- 2Al(OH)₃→Al₂O₃ + 3H₂O₂
B. Hall’s Process (Using Na₂CO₃)
Bauxite is leached with aqueous Na₂CO₃, forming sodium aluminate.
- Al₂O₃⋅2H₂O + Na₂CO₃ → 2NaAlO₂ + CO₂ + 2H₂
CO₂ is bubbled through the filtrate, precipitating Al(OH)₃.
- 2NaAlO₂ + 3H₂O + CO₂ → 2Al(OH)₃↓ + Na₂CO₃
Al(OH)₃ is heated at 1000°C, yielding Al₂O₃ (same as Bayer’s process).
2. Electrolytic Reduction of Alumina
Electrolysis of molten alumina (Al₂O₃) mixed with cryolite (Na₃AlF₆) and fluorspar (CaF₂) is carried out in a steel tank.
- The tank’s graphite lining acts as the cathode.
- Graphite rods act as the anode.
- Purpose of Cryolite & Fluorspar: These lower alumina’s melting point from >2000°C to ~1000°C, making the process more energy-efficient.
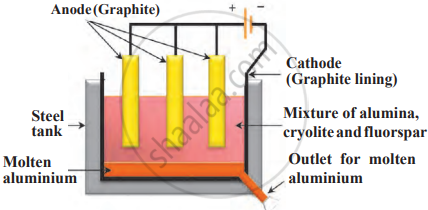
Extraction of aluminium
Electrode Reactions:
a. At Cathode (Reduction)
- Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al(l).
- Aluminium metal is deposited at the cathode and sinks to the bottom of the tank.
b. At Anode (Oxidation)
- 2O₂⁻→O₂+4e⁻
- Oxygen gas is released, which reacts with graphite anodes to form CO₂, requiring periodic replacement of the anodes.
Collection of Aluminium: Since molten aluminium is denser than the electrolyte, it settles at the bottom. It is periodically extracted through an outlet. This method efficiently extracts pure aluminium from its oxide (Al₂O₃) using electrolysis.
