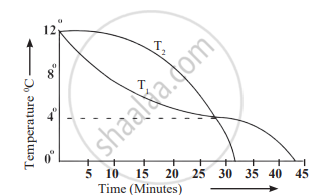
1. Aim: To understand how the density of water changes when salt is dissolved and how it affects the floating or sinking of objects, like a potato.
2. Requirements: two large glasses of water, 4-5 spoonfuls of salt, a potato, and a spoon for stirring.
3. Procedure
- Fill two glasses with water.
- Add 4-5 spoonfuls of salt to one of the glasses and stir until the salt completely dissolves.
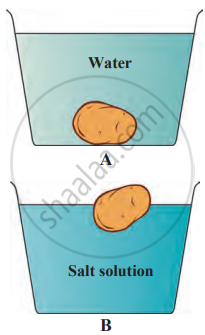
- Place a potato in the plain water (the second glass) and observe it sinking to the bottom.
- Now, take the potato out and place it in the saltwater glass. Observe what happens.
4. Observation: In the plain water, the potato sinks because the water's density is less than the potato's. However, in the salt water, the potato floats. This is because adding salt increases the density of the water, making it easier for the potato to float.
5. Conclusion: The experiment shows that adding salt to water increases its density, allowing objects like a potato to float more easily. This explains why it is easier to swim in the sea, which has salty water, than in a lake or well with fresh water. When salt dissolves in water, its particles spread throughout the water, mixing completely, which is known as dissolving. The salt (solute) dissolves in the water (solvent) to form a solution.