Topics
Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour (Chemistry)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
World of Living (Biology)
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Acids
- Bases (Alkalis)
- Indicators
- Properties of Acids
- Properties of Bases (Alkalis)
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Similarities and Differences Between Acids and Bases
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Salts
- Important Salts in Daily Life
- Preparation and Uses of Sodium Hydroxide
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
Metals and Non Metals
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- The Covalent Bond
- Prevention of Corrosion
Natural Phenomena (Physics)
Carbon and its Compounds
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- The Covalent Bond
- Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
- Allotropy and Allotropes of Carbon
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Diamond
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Graphite
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Fullerene
- Chains, Branches and Rings of Carbon Compound
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Properties of Carbon
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Soap
- Detergents
- Cleansing Action of Soap
Effects of Current (Physics)
Life Processes
- Living Organisms and Life Processes
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Mode of Nutrition in Plant
- Autotrophic Plants
- Heterotrophic Plants
- Different Ways of Taking Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- Swallowing and Peristalsis
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Breathing in Other Animals
- Osmoregulation
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Human Respiratory System
- Circulation in Animals
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Transport System in Plants
- Water absorbing organ
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Excretion
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Excretion
Natural Resources
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination in Human Being
- Human Nervous System
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Nerve Fibres
- Major Division of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- Reflex and Reflex Action
- Nervous Pathways in Reflexes
- Reflex Arc
- Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants
- Chemical Coordination
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Hormones in Animals
- Human Endocrine System
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Thymus Gland
Internal assessment
How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Reproductive Health
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
Heredity
- Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Sex Determination
- Organic Evolution
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Darwinism
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Speciation
- Evolution and Classiffication
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Paleobotany
- Evolution by Stages
- Human Evolution
Light - Reflection and Refraction
- Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Spherical Mirrors
- Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror
- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Image Formation by Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Image Formation by Convex Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Mirror Equation/Formula
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Introduction to Refraction of Light
- Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab
- Refractive Index
- Spherical Lens
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
The Human Eye and the Colourful World
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Care of the Eyes
- Refraction of Light Through a Prism
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Atmospheric Refraction
- Application of Atmospheric Refraction
- Scattering of Light and Its Types
- Applications of Scattering of Light
Electricity
- Electricity
- Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor
- Electrical Resistivity and Electrical Conductivity
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Effects of Electric Current
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Electrical Power
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Field
- Properties of magnetic lines of force
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
- Electric Generator
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
- Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor
- Types of Current
Our Environment
Sources of Energy
Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- Sustainability of Natural Resources
- Case Study: Ganga Pollution and Ganga Action Plan
- Solid Waste Management
- Five R’s of Waste Management
- Protecting our environment
- Forests: Our Lifeline
- Stakeholders of Forest
- Conservation of Forest
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Water Management (Conservation of Water)
- Fresh Water Management
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Petroleum
- Conservation of Coal, Petroleum, and Natural Resources
- Overview of Natural Resource Management
- Introduction
- Construction and Working
- Application
Introduction:
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy using the principle of electromagnetism.
Working Principle: The electric motor operates on the principle that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force that results in rotation.
This follows Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, which states:
- Thumb → Direction of motion (force)
- Index Finger → Direction of the magnetic field (North to South)
- Middle Finger → Direction of current

Electric motor in daily use
Construction and Working
Main Components of an Electric Motor:
- Rectangular Coil (ABCD): Conducts electric current and generates a magnetic field.
- Magnets (North and South Poles): Provide a strong magnetic field for interaction with current.
- Split rings (X and Y): Act as a commutator to reverse the direction of current after each half-rotation.
- Carbon Brushes (E and F): Maintain electrical contact between the coil and external circuit.
- Axle: Supports the coil and allows rotation.
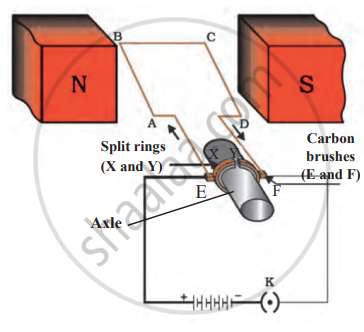
Electric motor: Principle and Working
Working of an Electric Motor:
Step 1: Current Flow in the Coil
When the circuit is closed, electric current flows through the carbon brushes (E and F) and split rings (X and Y) into the rectangular coil (ABCD). The coil is placed between the north and south poles of a magnet, creating a magnetic field.
Step 2: Force on the Coil due to Magnetic Field
According to Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule:
- The AB arm experiences a downward force.
- The CD arm experiences an upward force.
These opposite forces create a torque that rotates the coil anticlockwise.
Step 3: Role of the Split Ring Commutator
After half a rotation, the split rings switch their contact with the carbon brushes. This reverses the direction of current in the coil, ensuring that the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
Step 4: Continuous Rotation
As long as current flows, the coil keeps rotating, effectively converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. The rotation powers machines, fans, pumps, and other devices.
Application:
- It is used in fans, refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and mixers.
- Essential in electric vehicles, trams, and locomotives.
- Applied in water pumps, compressors, and conveyor belts.
- It is used in industrial machines, robotic arms, and automation systems.
- Plays a key role in MRI scanners, ventilators, and surgical tools.
- Found in CNC machines, printers, and AI-driven systems.
- It is used in power tools, elevators, and escalators.
- Integral to wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants.

