Topics
Gravitation
- Concept of Gravitation
- Force
- Motion and Rest
- Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Earth’s Gravitational force
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Waves
- Free Fall
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Weightlessness in Space
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration of Elements
- Groups and Electronic Configuration
- Periods and Electronic Configuration
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Reaction
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Galvanometer
- Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- Types of Current
- Electric Generator
Heat
Refraction of Light
Lenses
- Concept of Lenses
- Spherical Lens
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Combination of Lenses
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Persistence of Vision
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Reactions of Metal
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic Compounds
- Metallurgy
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Less Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Prevention of Corrosion
Carbon Compounds
- Carbon Compounds in Everyday Life
- Bonds in Carbon Compounds
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Hydrocarbons
- Structural Variations of Carbon Chains in Hydrocarbons
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- The IUPAC System of Nomenclature
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Macromolecules and Polymers
Space Missions
- Concept of Space Missions
- Artificial Satellites
- Types of Satellite
- Orbits of Artificial Satellites
- Space Launch Technology
- Space Missions Away from Earth
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 3
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Missions to Other Planets
- India and Space Technology
- Space Debris and Its Management
School of Elements
The Magic of Chemical Reactions
The Acid Base Chemistry
- Properties of Acids
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Acids, Bases and Their Reactivity
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Chemicals from Common Salt - Soap as a Salt
The Electric Spark
All about Electromagnetism
- Magnetic Force
- The Bar Magnet
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
Wonders of Light 1
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Spherical Mirrors
Wonders of Light 2
Striving for better Environment 1
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Radioactive Pollution and Effects
- Abatement of Pollution
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Early Moon Missions (Soviet Union & USA)
- Chandrayaan-1: India’s First Lunar Mission
- Objectives and Goals of Chandrayaan-1
Early Moon Missions (Soviet Union & USA)
The Moon, being the closest object to Earth, was the first target of space missions.
- The Soviet Union launched the Luna series. Luna 2 (1959) was the first to reach near the Moon.
- Between 1959 and 1975, 15 Luna missions studied the Moon’s gravity, radiation, and surface. Four of them returned with rock samples. All were unmanned.
- The USA conducted Moon missions between 1962 and 1972, including manned missions.
- In July 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to walk on the moon during the Apollo 11 mission.
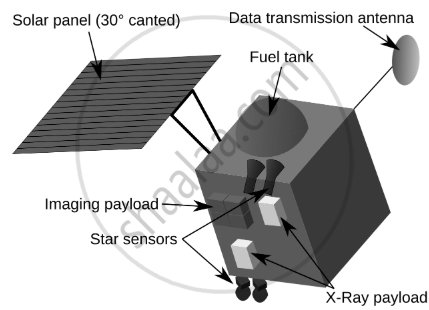
Chandrayaan-1: India’s First Lunar Mission
India’s space agency, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), launched its first moon mission named Chandrayaan-1 in 2008 under the Chandrayaan program.
|
Launch Date: 22 October 2008 at 00:52 UTC. Launch Site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. Launch Vehicle: PSLV-XL rocket (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle). Components: The mission had two parts:
|
|
Chandrayaan-1 |
Key Events:
- The orbiter entered lunar orbit on November 8, 2008.
- On November 14, 2008, the MIP was released and hit the Moon near Shackleton Crater at the south pole at 15:01 UTC.
- The impact site was named Jawahar Point.
- With this mission, India became the 5th country to reach the Moon’s surface after the Soviet Union (1959), USA (1962), Japan (1993), and ESA (2006).
Achievements:
- The most important discovery was the presence of water molecules in the moon’s surface soil.
- The orbiter operated for 312 days, although it was originally intended to last 2 years.
- The mission ended on 28 August 2009 due to technical issues like thermal problems and failure of the star tracker.
- Despite the early end, the mission achieved most of its scientific goals.
- Cost of the mission: ₹386 crore (~US$88.73 million).
Objectives and Goals of Chandrayaan-1
Main Objectives:
1. To design, develop, launch, and orbit a Moon spacecraft using an Indian-made launch vehicle.
2. To perform scientific experiments that would:
- Prepare a 3D map of both the near and far sides of the moon with high resolution (5–10 m).
- Conduct chemical and mineral mapping of the entire Moon surface, focusing on elements like magnesium, aluminium, silicon, calcium, iron, titanium, radon, uranium, and thorium.
- To test the impact of a Moon Impact Probe (MIP) for future soft landing missions.
- To increase scientific knowledge and boost India’s space technology.
Scientific Goals:
- High-resolution imaging and mapping of north and south polar regions (permanently shadowed areas).
- To search for surface or subsurface water ice, especially near the poles.
- Identification of chemical elements in lunar highland rocks.
- Study chemical layers of the lunar crust, including the South Pole Aitken Region (SPAR).
- Measure the height differences of lunar surface features.
- Observe the X-ray spectrum (above 10 keV) and get stereo images of most of the Moon’s surface.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [11]
Match the following:
| 1. | Chandrayaan – 1 | a. | Cosmonaut |
| 2. | Chandrayaan – 2 | b. | Mars Orbiter |
| 3. | Mangalyaan | c. | Dr. Mylsamy Annadurai |
| 4. | Rakesh Sharma | d. | Dr. Kailasa vadivoo Sivan |