Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 10 V cell of negligible internal resistance is connected in parallel across a battery of emf 200 V and internal resistance 38 Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of current in the circuit.
उत्तर
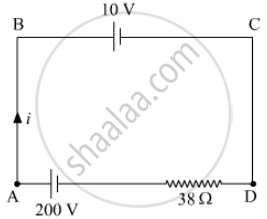
Applying KVL in the loop ABCDA
10 + 38i - 200 = 0
38i = 190
`i = 190/38 = 5A`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cell of emf 'E' and internal resistance 'r' is connected across a variable resistor 'R'. Plot a graph showing variation of terminal voltage 'V' of the cell versus the current 'I'. Using the plot, show how the emf of the cell and its internal resistance can be determined.
Plot a graph showing variation of voltage vs the current drawn from the cell. How can one get information from this plot about the emf of the cell and its internal resistance?
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ draws a current ‘I’. Write the relation between terminal voltage ‘V’ in terms of E, I and r ?
Two non-ideal batteries are connected in series. Consider the following statements:-
(A) The equivalent emf is larger than either of the two emfs.
(B) The equivalent internal resistance is smaller than either of the two internal resistances.
Two non-ideal batteries are connected in parallel. Consider the following statements:-
(A) The equivalent emf is smaller than either of the two emfs.
(B) The equivalent internal resistance is smaller than either of the two internal resistances.
A battery of emf 100 V and a resistor of resistance 10 kΩ are joined in series. This system is used as a source to supply current to an external resistance R. If R is not greater than 100 Ω, the current through it is constant up to two significant digits.
Find its value. This is the basic principle of a constant-current source.
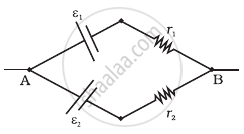
Two batteries of emf ε1 and ε2 (ε2 > ε1) and internal resistances r1 and r2 respectively are connected in parallel as shown in figure.
Three cells, each of emf E but internal resistances 2r, 3r and 6r are connected in parallel across a resistor R.
Obtain expressions for (i) current flowing in the circuit, and (ii) the terminal potential differences across the equivalent cell.
