Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Plot a graph showing variation of voltage vs the current drawn from the cell. How can one get information from this plot about the emf of the cell and its internal resistance?
उत्तर
Variation of voltage vs the current drawn from the cell shown below:
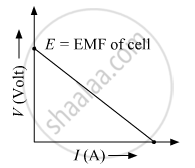
\[V = E - Ir\]
\[At, I = 0\]
\[V = E\]
\[\text { and }\]
\[r = \frac{E - V}{I}\]
The slope of the graph give the value of internal resistance and intercept on Y-axis gives the emf of the cell.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between emf and terminal voltage of a cell.
Six lead-acid types of secondary cells each of emf 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.015 Ω are joined in series to provide a supply to a resistance of 8.5 Ω. What are the current drawn from the supply and its terminal voltage?
A long straight current carrying wire passes normally through the centre of circular loop. If the current through the wire increases, will there be an induced emf in the loop? Justify.
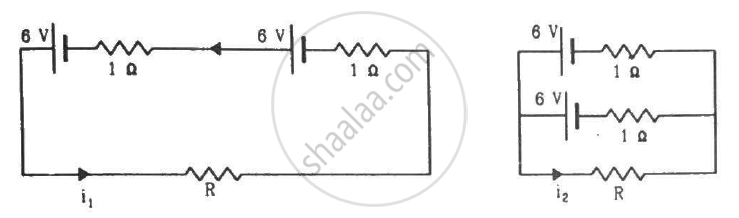
Find the value of i1/i2 in the following figure if (a) R = 0.1 Ω (b) R = 1 Ω and (c) R = 10 Ω. Note from your answers that in order to get more current from a combination of two batteries, they should be joined in parallel if the external resistance is small and in series if the external resistance is large, compared to the internal resistance.
Apply the first law of thermodynamics to a resistor carrying a current i. Identify which of the quantities ∆Q, ∆U and ∆W are zero, positive and negative.
Do all thermocouples have a neutral temperature?
A cell having an emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a variable external resistance R. As the resistance R is increased, the plot of potential difference V across R is given by ______.
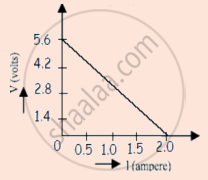
A straight line plot showing the terminal potential difference (V) of a cell as a function of current (I) drawn from it, is shown in the figure. The internal resistance of the cell would be then ______.
Three cells, each of emf E but internal resistances 2r, 3r and 6r are connected in parallel across a resistor R.
Obtain expressions for (i) current flowing in the circuit, and (ii) the terminal potential differences across the equivalent cell.
